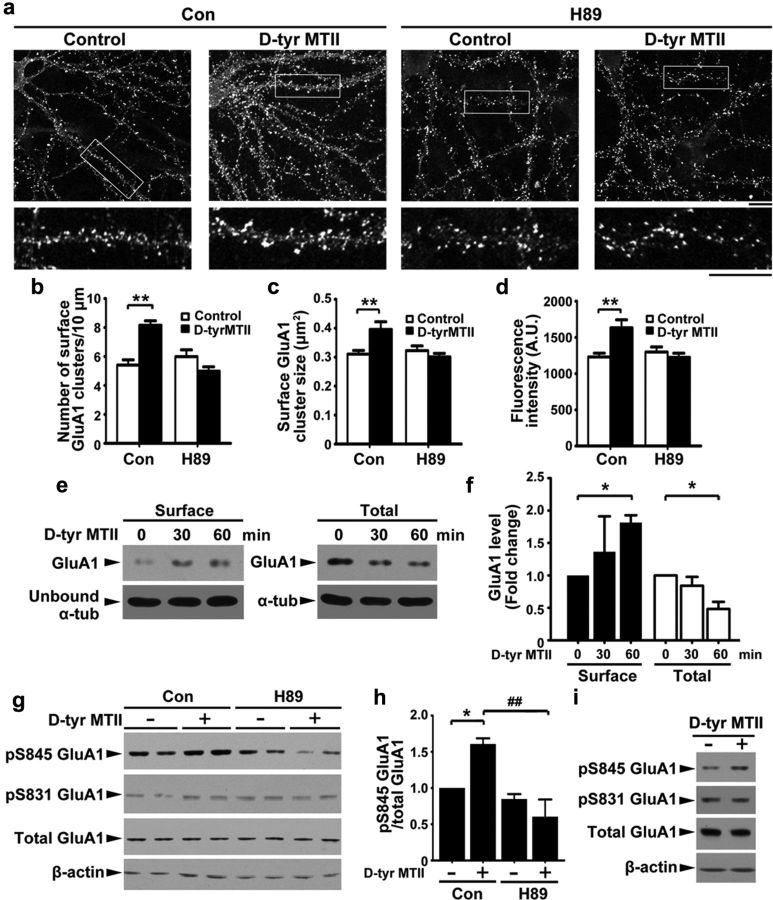
Figure 3.
MC4R regulates surface levels of GluA1 through PKA-dependent phosphorylation. a–d, Hippocampal neurons were incubated with d-Tyr MTII (100 nm) and H89 (10 μm) for 2 h and then stained for surface GluA1. a, Representative images. Scale bar, 10 μm. b–d, Quantification of density (b), size (c), and intensity (d) of surface GluA1 clusters. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, d-Tyr MTII versus control (two-way ANOVA); n = 10 neurons from each experiment, two experiments). e, Surface and total proteins of hippocampal neurons after d-Tyr MTII treatment were collected and subjected to Western blot analysis for GluA1. f, Fold change (three experiments; *p < 0.05 versus 0 min, one-way ANOVA with Student-Newman–Keuls test. g, h, Hippocampal neurons were cotreated with d-Tyr MTII and H89 for 1 h. g, Western blot analysis. h, Quantitative analysis; *p < 0.05 d-Tyr MTII (+) versus no treatment (−), two-way ANOVA; ##p < 0.01, versus d-Tyr MTII, one-way ANOVA with Student-Newman–Keuls test. i, d-Tyr MTII increased level of pSer845 GluA1 in cultured hippocampal slices (7 DIV).