Figure 4.
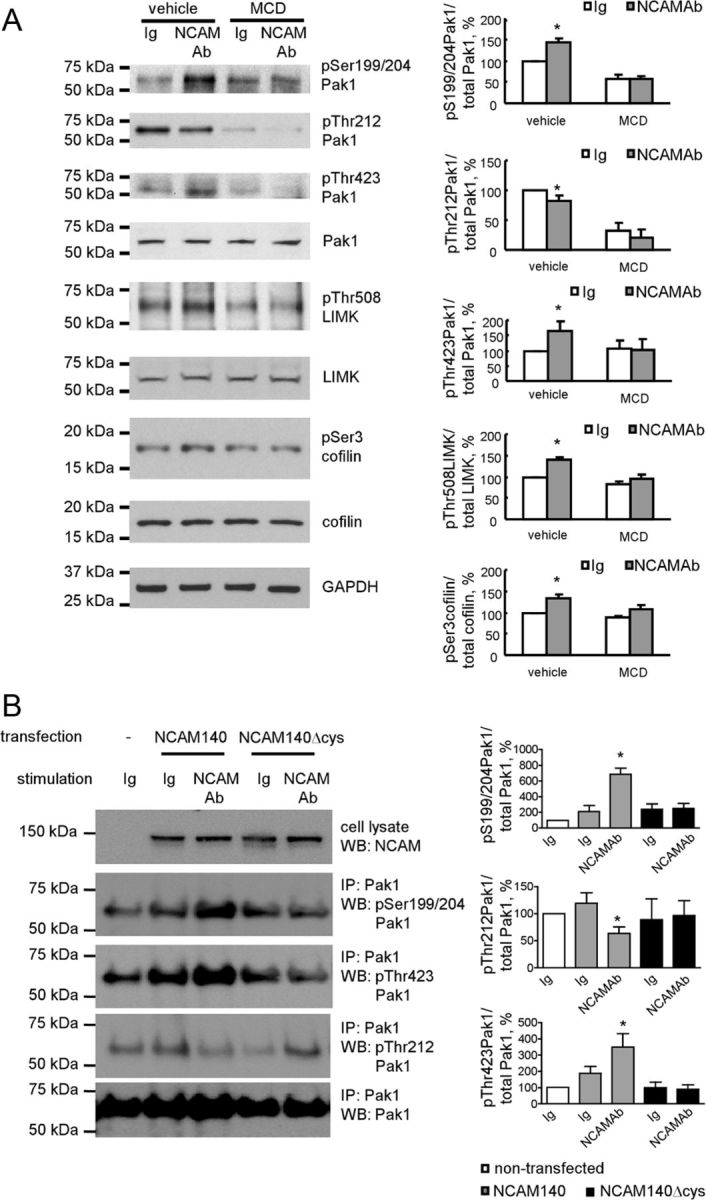
Association of NCAM with lipid rafts is required for NCAM-dependent Pak1 pathway induction. A, Western blot analysis of lysates of growth cones from NCAM+/+ mouse brains probed with the indicated antibodies. Growth cones were treated with vehicle (water used to dilute MCD) or 5 mm MCD and incubated with polyclonal antibodies against NCAM or nonimmune Ig. Graphs show quantitation of the blots from five experiments. Mean + SEM values normalized to the values for vehicle-treated and nonimmune Ig-treated growth cones set to 100% are shown. *p < 0.05, paired t test compared with the corresponding probes from nonimmune Ig-treated growth cones. Note that MCD inhibits NCAM antibody-induced phosphorylation of Pak1 at Ser199/204 and Thr423, LIMK1 at Thr508, and cofilin at Ser3. B, Western blot analysis of lysates and Pak1 immunoprecipitates (IP) from nontransfected B35 cells and B35 cells transfected with NCAM140 or NCAM140Δcys probed with the indicated antibodies. Cells were treated with nonimmune Ig or function-triggering polyclonal antibodies against NCAM. Graphs show quantitation of the blots from three experiments. Mean + SEM levels of phosphorylated Pak1 normalized to levels of total immunoprecipitated Pak1 are shown. Values for nontransfected and nonimmune Ig-treated cells were set to 100%. *p < 0.05, ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparison test. Note NCAM antibody-induced phosphorylation of Pak1 at Ser199/204 and Thr423, and inhibition of Pak1 phosphorylation at Thr212 in NCAM140-transfected cells but not NCAM140Δcys-transfected cells.
