Figure 6.
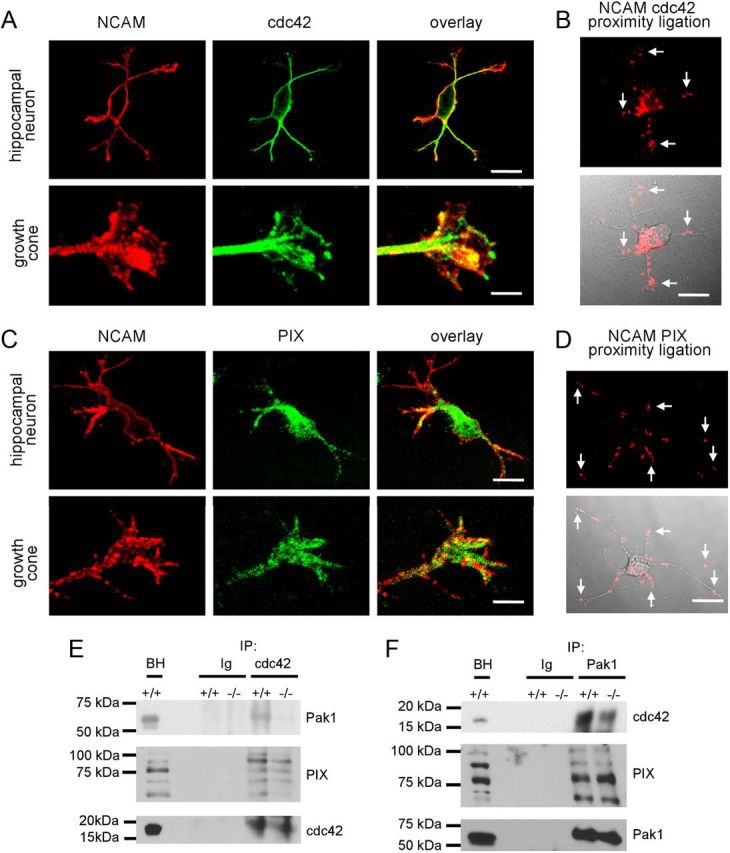
Pak1/cdc42/PIX complex formation is inhibited in NCAM−/− versus NCAM+/+ brains. A, C, Examples of hippocampal neurons and growth cones of hippocampal neurons maintained for 1 d in culture colabeled with antibodies against NCAM and cdc42 (A) or PIX (C). Note clusters of NCAM overlapping with accumulations of Cdc42 and PIX in growth cones (yellow). Scale bars: neurons, 20 μm; growth cones, 5 μm. B, D, Proximity ligation assays with antibodies against the intracellular domain of NCAM and cdc42 (B) or PIX (D). Arrows show examples of NCAM/cdc42 and NCAM/PIX complexes in growth cones. Proximity ligation fluorescence signals alone (top) or in combination with differential interference contrast images (bottom) are shown. E, F, Cdc42 and Pak1 immunoprecipitates (IP) from 1-d-old NCAM+/+ and NCAM−/− mouse brains were probed with antibodies against Pak1, cdc42, and PIX by Western blot. Mock immunoprecipitation with nonimmnune Ig served as control. Note reduced coimmunoprecipitation of Pak1 and PIX with cdc42 (E) and reduced coimmunoprecipitation of cdc42 with Pak1 (F) from NCAM−/− versus NCAM+/+ brains. BH, brain homogenates.
