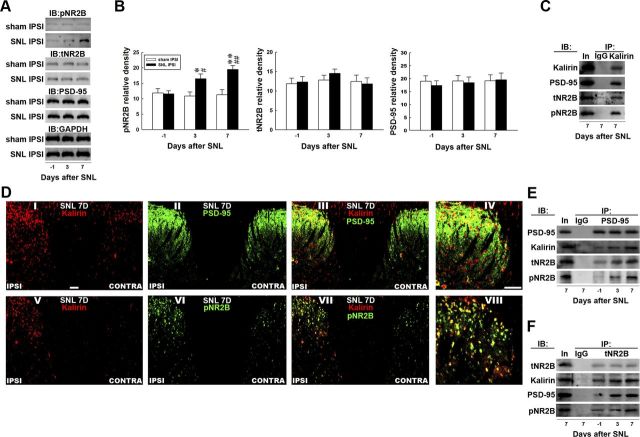
Figure 3.
Nerve ligation provokes dorsal horn kalirin–PSD-95 and PSD-95–NR2B coupling. A, Representative Western blot showing the expression of pNR2B, tNR2B, and PSD-95 after spinal nerve ligation (SNL IPSI) or sham operation (Sham IPSI). The lysates of the ipsilateral dorsal horn were obtained on the day before the operation and 3 and 7 d after the operation and were probed with pNR2B-specific, tNR2B-specific, and PSD-95-specific antibodies. The level of GAPDH was used as a loading control. IB, immunoblotting. B, Statistical analysis revealed that spinal nerve ligation statistically increased the band intensity of pNR2B measured on days 3 and 7 postsurgery when compared with the presurgery control (day −1; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs day −1, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs sham operation, n = 7). In contrast, nerve ligation did not affect the levels of tNR2B (p > 0.05 vs day −1, n = 7) or PSD-95 (p > 0.05 vs day −1, n = 7) at these time points. Moreover, the sham operation (sham IPSI) had no effect on the expression of the measured proteins (all p > 0.05, vs day −1, n = 7). The data show mean ± SEM. C, Coimmunoprecipitation of kalirin, PSD-95, tNR2B, and pNR2B in the ipsilateral spinal cord. Dorsal horn samples obtained 7 d after operation were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against kalirin (IP: kalirin) or control IgG (IP: IgG) and were then probed with PSD-95, tNR2B, and pNR2B antibodies. The PSD-95-specific, tNR2B-specific, and pNR2B-specific antibodies labeled immunoreactivity in the immunoprecipitates recognized by the kalirin-selective antibody but not in those recognized by control IgG. In, input sample. D, Spinal nerve ligation notably enhanced the immunoreactivity of kalirin (I and V, red) and pNR2B (VI, green) but not PSD-95 (II, green) in the ipsilateral dorsal horn (IPSI) compared with the contralateral dorsal horn (CONTRA) of the spinal sections obtained 7 d after surgery (SNL 7D). Overlay images showing kalirin fluorescence costained with PSD-95 and pNR2B immunoreactivity (III and VII, yellow). IV, VIII, Amplified images of III and VII, respectively. Each of these immunofluorescence images was replicated in seven sample preparations with similar results each time. Scale bar, 50 μm; thickness, 50 μm. E, F, Dorsal horn samples obtained on the day before operation and 3 and 7 d after operation were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against PSD-95 (IP:PSD-95), tNR2B (IP: tNR2B) or control IgG (IP: IgG) and were then probed with PSD-95, kalirin, tNR2B, and pNR2B antibodies. Spinal nerve ligation enhanced the kalirin-labeled, tNR2B-labeled, and pNR2B-labeled immunoreactivity in the PSD-95 immunoprecipitates and the kalirin-labeled, PSD-95-labeled, and pNR2B-labeled immunoreactivity in the tNR2B immunoprecipitates when compared with the presurgery control. However, no detectable immunoreactivity was labeled by these antibodies in the precipitation recognized by the control IgG. In, input sample.