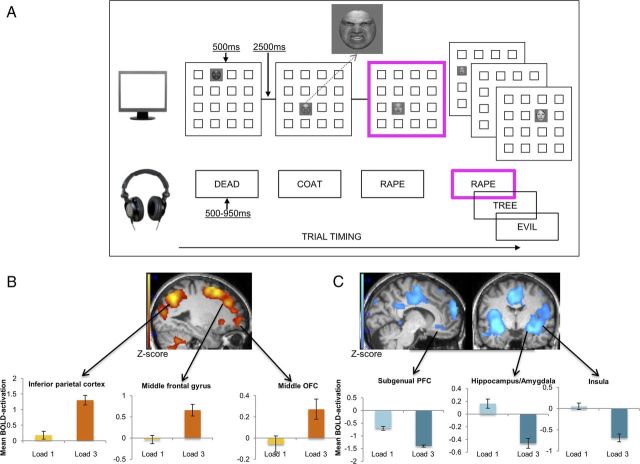
Figure 1.
A, Task design of the eWM training (dual n-back) task for a sample training block where n-back = 1. Stimuli with a bold pink border represent target stimuli for the current block. Participants respond with a button press if the target stimulus in either or both modalities matches the stimulus n positions back. In this n-back = 1 example, there is a match because, for the visuospatial modality, the current face appears in the same location as the face 1-position back; and for the auditory target, the word (RAPE) is the same as the word one-back. B, C, Task-demand-related BOLD activation that was observed comparing conditions of lower task-demand (n-back = 1) and higher task-demand (n-back = 3) at pre-training. All reported BOLD activation was significantly different across these conditions at the whole-brain level, with significance levels corrected for false discovery rates at PFDR < 0.05. Activation increases (B) and activation decreases (C) in condition n-back = 3 compared with n-back = 1. For a full overview of differential activation, see Table 1. Error bars indicate SEM.