Figure 7.
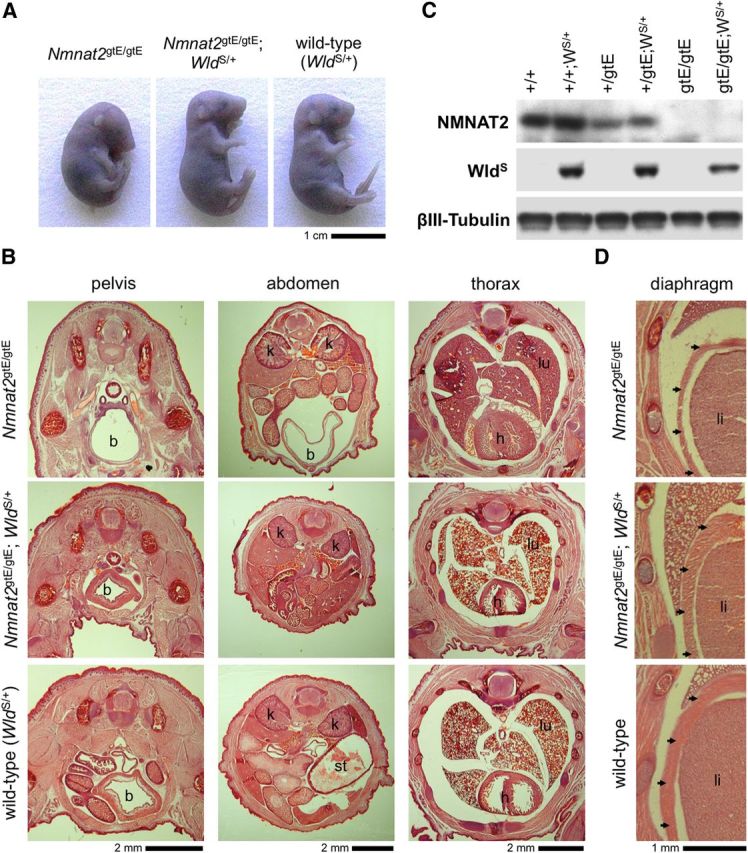
Gross morphological defects found in newborn pups lacking NMNAT2 are rescued by WldS expression. A, Posture of Nmnat2gtE/gtE, Nmnat2gtE/gtE;WldS/+, and wild-type (WldS/+) E18.5 embryos. All Nmnat2gtE/gtE;WldS/+ E18.5 embryos and newborn pups observed to date (n = 13) had a normal posture. Heterozygosity for WldS does not affect the gross appearance of wild-type or Nmnat2+/gtE embryos (which are also normal; data not shown). B, Hematoxylin and eosin-stained pelvic, abdominal, and thoracic cryosections from newborn Nmnat2gtE/gtE, Nmnat2gtE/gtE;WldS/+, and wild-type (WldS/+) pups. A distended bladder (b) can be seen to extend to the level of the kidneys (k) in the abdomen of the Nmnat2gtE/gtE pup. There is also reduced muscle mass in the thigh, pelvis, and abdominal walls, and collapsed lungs (lu) are indicative of a failure to breathe. The Nmnat2gtE/gtE;WldS/+ pup appears similar to the wild-type with a nondistended bladder, normal muscle mass, and lungs (lu) that show clear signs of inflation. A distended stomach (st) can be seen in the abdomen of the wild-type pup. C, Immunoblot showing selective expression of WldS in newborn wild-type (+/+), Nmnat2+/gtE, and Nmnat2gtE/gtE pups heterozygous for WldS (WS/+). βIII-Tubulin represents the sample control, and NMNAT2 levels confirm the Nmnat2 genotype. D, Hematoxylin and eosin-stained cryosections showing an underdeveloped diaphragm in a newborn Nmnat2gtE/gtE pup but normal diaphragms in newborn Nmnat2gtE/gtE;WldS/+ and wild-type pups. The diaphragm (arrowhead) lies between the liver (li), the lungs (top), and the ribcage (left) in these sections. B, D, Images are representative of at least n = 3 per genotype.
