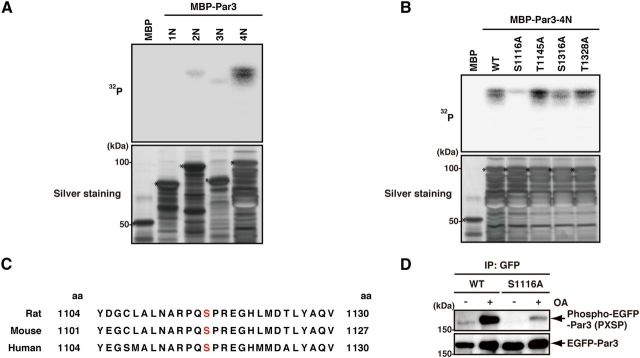
Figure 2.
Identification of the phosphorylation site of Par3 by ERK2. A, The direct phosphorylation of Par3 by ERK2. Purified MBP or MBP-Par3 deletion mutants were incubated with recombinant ERK2 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP in vitro. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and silver staining (bottom) followed by autoradiography (top). Asterisks indicate intact MBP-fusion proteins. B, The phosphorylation of Par3 point mutants by ERK2. Purified MBP, MBP-Par3-4N-WT -S1116A, -T1145A, -S1316A, or -T1328A was incubated with recombinant ERK2 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP in vitro. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and silver staining (bottom) followed by autoradiography (top). Asterisks indicate intact MBP-fusion proteins. C, The alignment of ERK2 phosphorylation sites in Par3 homologs (rat, mouse, human). D, The phosphorylation of Par3-WT or -S1116A in COS7 cells. COS7 cells were transfected with EGFP-Par3-WT or -S1116A and cultured for 24 h. The cells were serum-starved for 24 h and then treated with or without 1 μm OA for 2 h. Cell lysates were incubated with anti-GFP antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-MAPK/CDK substrates and anti-GFP antibodies.