Figure 4.
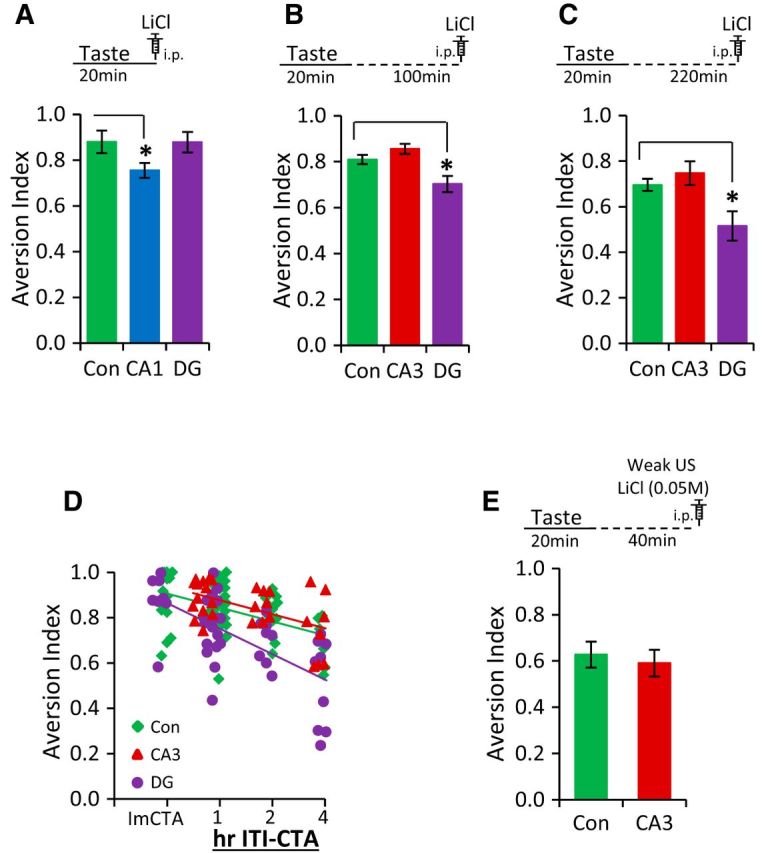
NMDA receptor-mediated function in DG is critical for the temporal context association in CTA learning and memory. A, Top depicts the time course of immediate CTA conditioning trial. CA1-NR1 KOs exhibited an attenuation of CTA memory, whereas the DG-NR1 KOs showed a normal CTA memory after immediate CTA training. B, Top depicts the time course of the 2 h ITI-CTA conditioning trial. DG-NR1 KOs showed impaired CTA memory in the 2 h ITI-CTA. CA3-NR1 KOs were not different from control mice. C, Top depicts the time course of the 4 h ITI-CTA conditioning trial. DG-NR1 KOs showed impaired CTA memory in the 4 h ITI-CTA. CA3-NR1 KOs were not different from control mice. D, Scatter plots are superimposed appropriately. ImCTA on the x-axis represents immediate CTA. The strength of CTA memory was negatively correlated with the interval between taste and LiCl injection in control mice, CA3-NR1 KOs, and DG-NR1-KOs. In addition, the progressive nature of the phenotype of DG-NR1 KOs can be seen. E, Top depicts the weak CTA conditioning trial. CA3-NR1 KOs exhibited a normal CTA memory following weak CTA training. Con, CA1, CA3, and DG represent control mice, CA1-NR1 KOs, CA3-NR1 KOs, and dentate gyrus-NR1 KOs, respectively. *p < 0.05.
