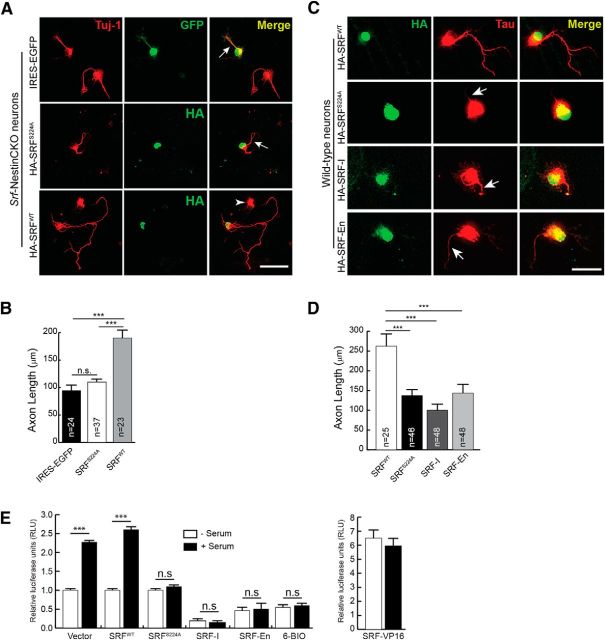
Figure 2.
Serine 224 is required for SRF function. A, SRFS224A mutant cannot rescue axonal growth deficits of SRF-deficient neurons. P0.5 hippocampal neurons from Srf-NestinCKO mice were transfected with IRES-EGFP empty vector, HA-SRFWT, or HA-SRFS224A. Cells were fixed and immunostained for GFP or HA (green) to visualize transfected cells and anti-Tuj1 (red) at 4 DIV. Axonal growth deficits exhibited by SRF-deficient neurons were rescued by SRFWT alone and not by empty vector or SRFS224A (arrows). Arrowhead indicates an untransfected cell. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Quantitation of axon length from A. n = 4 mice; “n” in the bars indicates the number of cells measured for statistics. Error bars indicate SEM. ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey post-test analysis). n.s., Not significant. C, SRFS224A functions as a dominant mutant when expressed in wild-type hippocampal neurons. Cells were transfected with HA-SRFWT or HA-SRFS224A and grown for 4 DIV. Cells were fixed and immunostained with anti-HA (green) and anti-Tau (red) antibodies. HA-SRFS224A expression attenuated axonal growth (arrows). Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Data quantified from C. Error bars indicate SEM. ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey post-test analysis). E, Inhibiting GSK-3 activity or mutating serine 224 to alanine abolishes SRF transcriptional activity. HEK293T cells were transfected with 5×-SRE luciferase and Renilla luciferase (for transfection efficiency) and treated with either 6-BIO or cotransfected with control vector, SRFWT, SRF-S224A, or SRF-VP16. 6-BIO treatment blocked serum-induced SRF-transcriptional activity. Whereas vector and SRFWT transfected cells showed normal activation of an SRE reporter, the SRFS224A mutant was severely compromised in activating transcription. Expression of constitutively active SRF-VP16 served as the control. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM.