Figure 8.
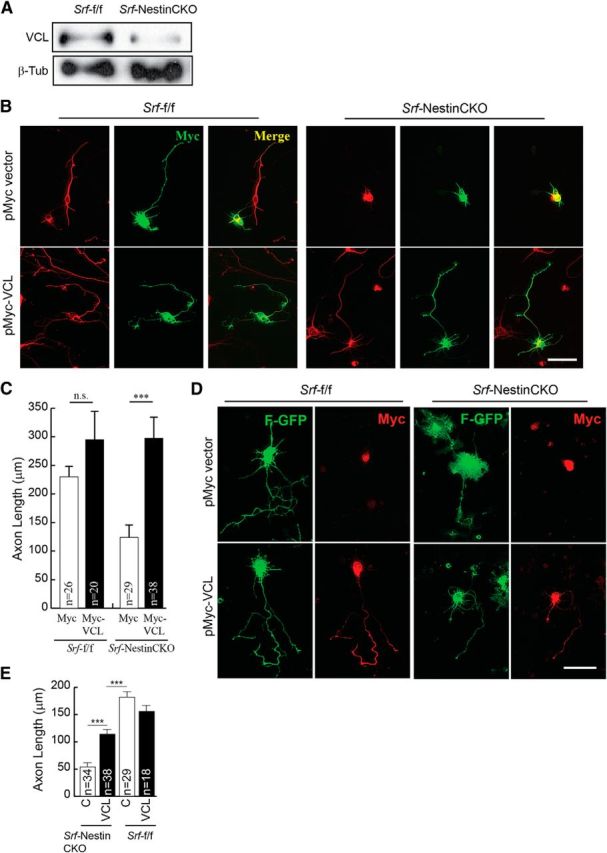
Vinculin is sufficient to promote axonal growth in SRF-deficient neurons. A, Western blot of total brain lysate showing reduced Vcl expression in Srf-NestinCKO mice compared with control littermates. B, P0.5 hippocampal neurons from Srf-NestinCKO and Srf-f/f mice were cotransfected with empty vector (pMyc) or pMyc-VCL and cultured for 4 DIV on poly-d-lysine and laminin. Cells were fixed and immunostained for Tuj1 (red) and Myc (green). Expression of Vcl but not empty vector was able to promote axon growth. Scale bar, 25 μm. C, Quantitation of B. Error bars indicate SEM. ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey post-test analysis). n.s., Not significant. D, Vinculin only partially rescues axonal growth in SRF-deficient neurons in the absence of laminin. P0.5 hippocampal neurons from Srf-NestinCKO and Srf-f/f mice were cotransfected with empty vector (pMyc) or pMyc-VCL along with farnesylated-GFP (F-GFP) and cultured for 4 DIV on poly-d-lysine alone without laminin. Cells were fixed and immunostained for GFP (green) to visualize neuronal morphology and Myc (red) for transfected cells. Expression of VCL, but not empty vector, could partially rescue axonal growth in the absence of laminin, suggesting a role for laminin–integrin signaling downstream of VCL in promoting axon growth. Scale bar, 25 μm. E, Quantitation of axon length in D. ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey post-test analysis).
