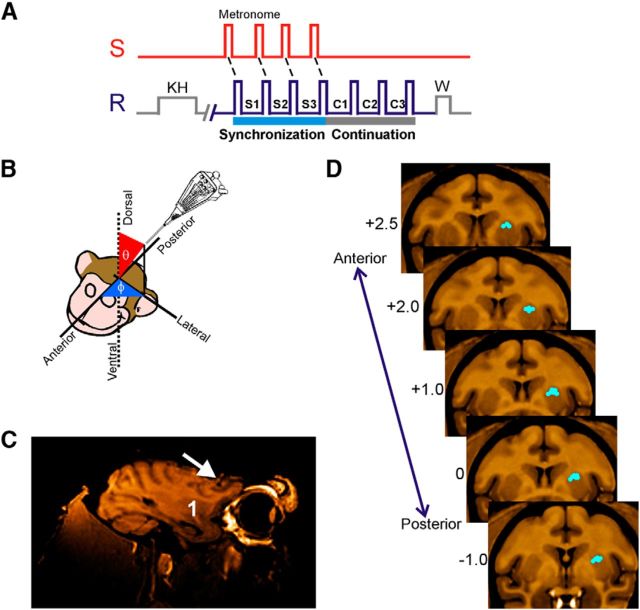
Figure 1.
SCT and location of recording sites. A, Sensory and motor events in the SCT. S, Stimuli with an isochronous interval; R, push-button press; KH, key hold; W, reward; S1–S3, intertap intervals of the synchronization phase; C1–C3, intervals of the continuation phase. B, Navigation method to reach the dorsal putamen. Guiding cannulae were oriented in spherical coordinates with respect to the anterior–posterior, medial–lateral, and dorsal–ventral axes of the monkey's head. MRI was used to calculate the appropriate coordinates and to verify the trajectory. C, MRI in the parasagittal plane where the white arrow points to the trajectory of an MRI-compatible cannula and the number 1 is located on the putamen. D, Representative standard coronal sections of the macaque brain (Frey et al., 2011) illustrating the area in which LFPs were recorded for one monkey. The numbers to the left are millimeters with respect to the anterior commissure. Blue dots correspond to the recording sites.