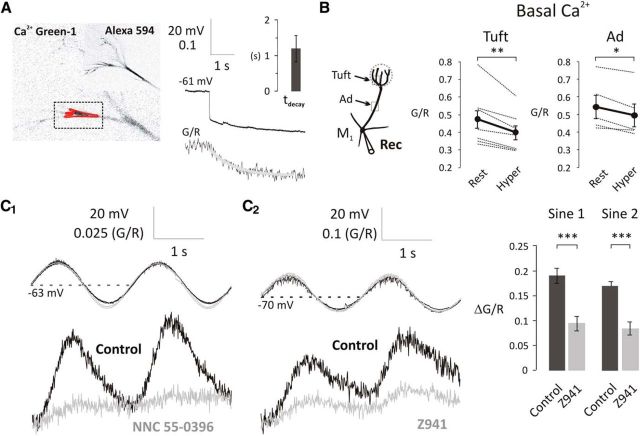
Figure 4.
T-type Ca2+ channels modulate the basal [Ca2+] at subthreshold potentials in the primary dendrite of mitral cells. A, Mitral cells were loaded with Alexa-594 and Ca2+ Green-1 as shown on the fluorescent images (left). Rectangle represents the scanned area; red polygon represents the region of interest. Basal [Ca2+] was expressed as G/R. A 4-s-long hyperpolarizing step from Vrest to Vhyper caused a reduction in basal [Ca2+] (τdecay = 1.20 s, n = 5). B, A 4-s-long hyperpolarizing step significantly decreased the basal [Ca2+] in the apical dendrite and tuft. Black dots connected with thick black lines indicate the mean of 7 and 5 individual experiments (thin lines) in the apical tuft and apical dendrite (Ad), respectively. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. C1, C2, Sinusoidal modulation of membrane potential above and below normal resting potential modulates basal [Ca2+]. Voltage-dependent increases in basal [Ca2+] are attenuated by T-type channel blockers NNC 55–0396 (50 μm) and Z941 (10 μm). Bar charts on the right represent the population effect of Z941 on the amplitudes of subthreshold Ca2+ influx (control, black, n = 4; Z941, gray, n = 4, 5–20 min bath application). ***p < 0.001.