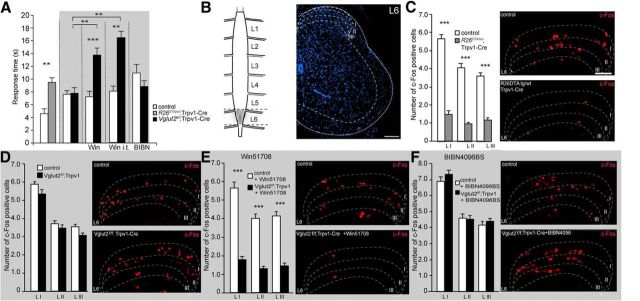
Figure 2.
TRPV1 neurons are crucial for intact cold transmission, which is dependent on VGLUT2-mediated signaling from Trpv1–Cre neurons and substance P. A, R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre mice are less sensitive to cold pain compared with control mice (n = 6 per genotype), whereas Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre do not differ from control littermates (n = 7 per genotype). Win51708 injections resulted in decreased responses to cold in Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre (n = 7 per genotype). Pretreatment with BIBN4096BS did not alter the behavior of either Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre mice or control littermates (n = 6 per genotype). The animals were treated with vehicle for possible side effects; however, no changes in the behavior was observed after vehicle treatment. B, Schematic representation of c-Fos expression in the spinal cord. The major peak of expression was observed in a lumbar segment L6 and initial sections of sacral segment S1. C, Deletion of TRPV1 neurons resulted in a decreased number of c-Fos cells in the dorsal horn in laminae I–III in R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre mice compared with control mice (n = 2 per genotype, 46 sections for controls, 39 sections for R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre). C, Conversely, ablation of VGLUT2 from TRPV1 neurons did not affect the expression of c-Fos in dorsal horn in Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre mice compared with controls (n = 2 per genotype, 36 sections for controls, 51 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre. E, Pretreatment with the substance P antagonist Win51708 induced a decreased response of c-Fos in Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre compared with controls (n = 2, 45 sections for controls, 42 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre. F, Interestingly, injections of BIBN4096BS did not affect the expression of c-Fos in Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre compared with controls (n = 2 per genotype, 51 sections for control, 45 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre). Data represent means ± SEMs. Shown are Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre and R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre (gray) and the respective controls (white). ***p < 0.001. Mann–Whitney two-tailed test (A–D). Scale bars: B, 72 μm; C–F, 120 μm.