Figure 5.
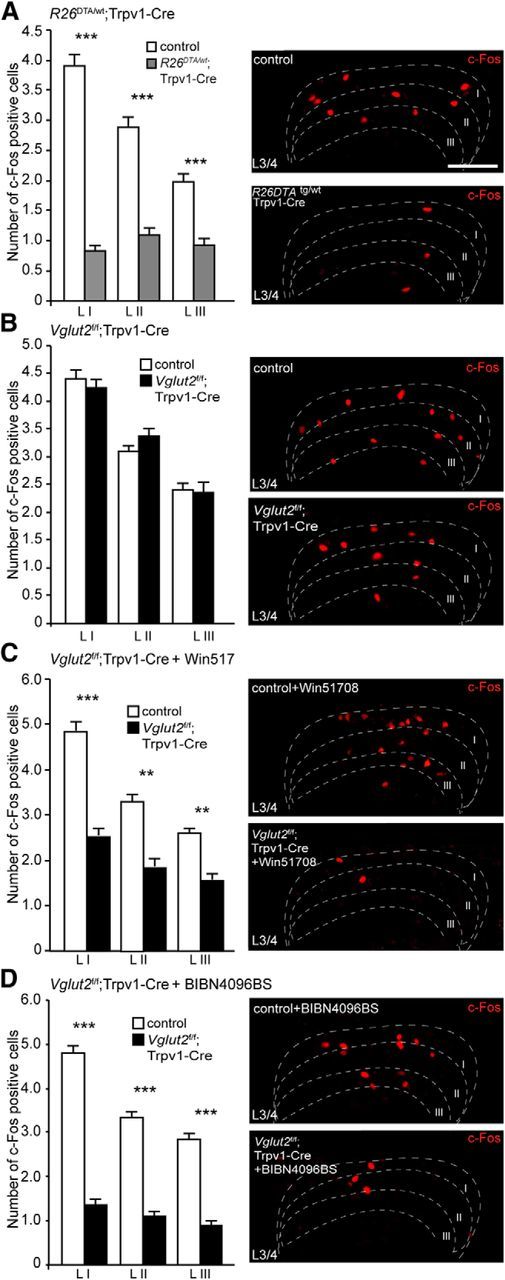
The contribution of VGLUT2, substance P, and CGRP to the development and transmission of Formalin-induced inflammation is apparent at second-order neurons. A, R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre mice were shown to have decreased levels of c-Fos-positive cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord compared with control animals (n = 2 per genotype, 51 sections for controls, 41 sections for R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre; n = 2 per genotype, 52 sections for controls, 42 sections for R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre). B, Ablation of Vglut2 from Trpv1–Cre neurons did not result in any significant changes in the number of observed c-Fos cells between Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre and control mice (n = 2 per genotype, 58 sections for controls, 52 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre; n = 2 per genotype, 59 sections for controls, 53 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre). C, Injection of Win51708 before the experiment resulted in a decreased number of c-Fos activated cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord (n = 2 per genotype, 59 sections for controls, 47 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre; n = 2 per genotype, 60 sections for controls; 48 for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre). D, Similarly, pretreatment with BIBN4096BS resulted in a decreased number of c-Fos activated cells in Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre compared with controls (n = 2 per genotype, 49 sections for controls, 57 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre; n = 2 per genotype, 50 sections for controls, 73 sections for Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre). Mann–Whitney test, two-tailed. **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.001. Data represent means ± SEMs. Shown are Vglut2f/f;Trpv1–Cre (black), R26DTA/wt;Trpv1–Cre (gray), and respective controls (white). Scale bar, 100 μm.
