Figure 2.
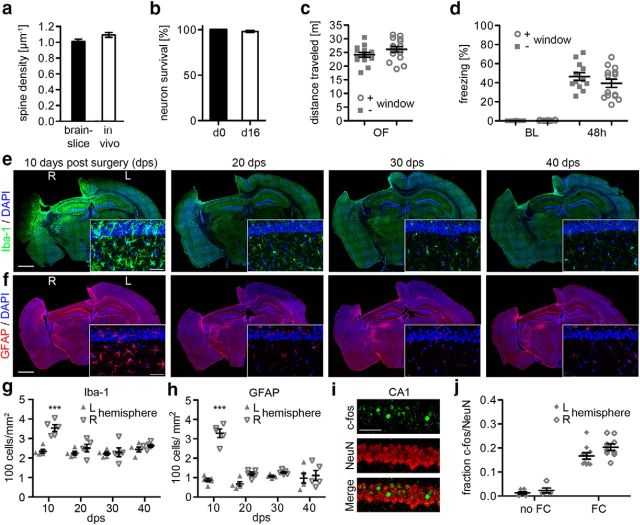
Secondary effects of window implantation. a, Spine density of radial oblique dendrites in fixed brain slices without surgery compared with spine densities in vivo (p > 0.05, n = 5 mice/group, t test). b, Survival of YFP-positive neurons after 16 d (p > 0.05, n = 6 mice, t test). c, Open-field (OF) behavior of mice with or without hippocampal window surgery (p > 0.05, n = 14–15 mice/group, t test). d, Freezing rates of mice with or without window surgery at baseline (BL) and 48 h after fear conditioning (p > 0.05, n = 12–14 mice/group, 1-way ANOVA). e, f, Microgliosis and astrogliosis at 10, 20, 30, and 40 d after implanting a hippocampal window. Brain sections were stained with Iba1 (microglia, green), GFAP (astrocytes, red), and DAPI (nuclei, blue). Zoom of hippocampal CA1 layer. g, h, Quantification of Iba1-positive (g) and GFAP-positive (h) cells in the hippocampus of the left (L) and right (R) hemisphere at 10, 20, 30, and 40 d postsurgery (10 d postsurgery: p < 0.001, n = 5 mice/group, 2-way ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-test). i, Staining of hippocampal CA1 neurons for c-Fos and NeuN. j, Fraction c-Fos-positive of NeuN-positive CA1 neurons in naive mice (no FC) and in mice after fear conditioning (FC), comparing the right (R) hemisphere with implanted window and left (L) hemisphere without window. (p > 0.05, n = 5–10 mice/group, 2-way ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-tests). Scale bars: e, f, overview, 1 mm; e, f, zoom, 50 μm; i, 50 μm.