Figure 6.
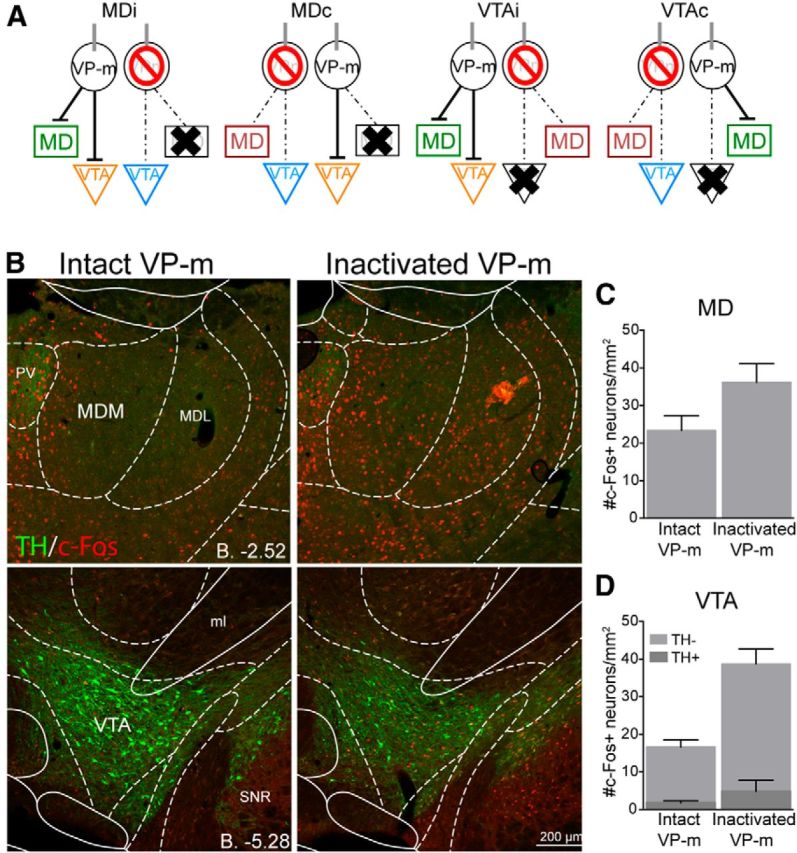
Experiment 2. c-Fos expression in the MD and VTA after VP-m inactivation. A, Three regions in each animal were quantified. Depending on the side of the infusion and lesion, similar regions (green, orange, blue, or red) across groups were collapsed for analysis. B, Photomicrographs of c-Fos expression in the MD and VTA after an infusion of muscimol into the VP-m (right) compared with no manipulation of the VP-m (left). C, D, Quantification of c-Fos expression in the MD with an intact ipsilateral VP-m (n = 16) compared with an inactivated ipsilateral VP-m (n = 16) found an increase in c-Fos expression after VP-m inactivation. Neurons in the VTA were further separated as those that were TH+ or TH−. Similarly, c-Fos expression in both types of neurons was elevated in the VTA with an intactivated ipsilateral VP-m (n = 16) compared with an intact ipsialteral VP-m (n = 15). MDM, Mediodorsal thalamus nucleus, medial part; MDL, mediodorsal thalamus nucleus, lateral part; ml, medial lemniscus; PV, paraventricular thalamic nucleus; SNR, substantia nigra pars reticula part.
