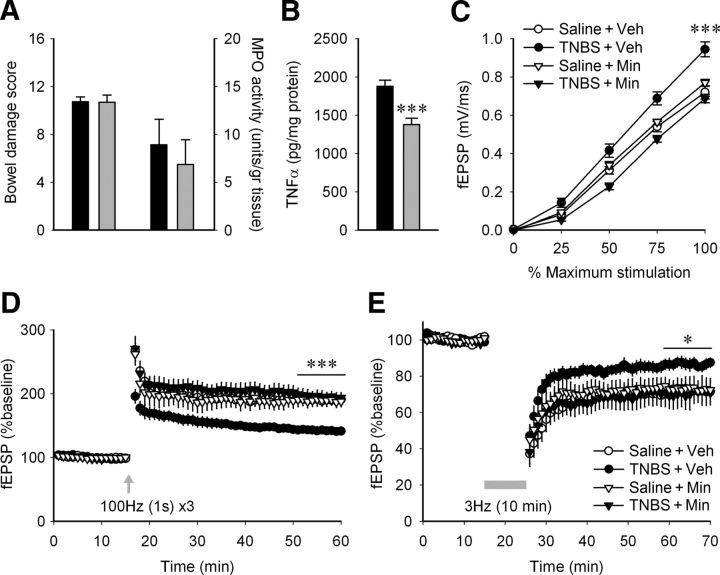
Figure 6.
Daily minocycline treatment abolishes the effect of peripheral inflammation on hippocampal synaptic transmission and plasticity without affecting the inflammation intensity. A, There was no significant difference in bowel damage score (TNBS + vehicle, n = 8; TNBS + minocycline, n = 8; t test, p = 0.960) or MPO activity levels (t test, p = 0.608) between the colitic animals with vehicle injections (black bars) and minocycline (25 mg/kg/12 h, i.p.; gray bars). B, Minocycline lowers the level of TNFα in hippocampal tissue from animals with peripheral inflammation (n = 8; TNBS + vehicle, black bars; TNBS + minocycline, gray bars). ***p = 0.0007 (t test). C, Minocycline inhibits the increase in fEPSP caused by peripheral inflammation [saline + vehicle (Veh), n = 8 slices, 5 rats; saline + minocyline (Min), n = 7 slices, 4 rats; TNBS + vehicle, n = 10 slices, 5 rats; TNBS + minocycline, n = 8 slices, 5 rats]. ***p < 0.001 when the TNBS + vehicle group was compared to any of the other three (two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc). D, Minocycline inhibits the decrease in LTP caused by peripheral inflammation (saline + vehicle, n = 7 slices, 5 rats; saline + minocycline, n = 6 slices, 4 rats; TNBS + vehicle, n = 9 slices, 5 rats; TNBS + minocycline, n = 7 slices, 5 rats). The final 10 min after LTP induction for each slice was averaged, and the four treatment groups were compared using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test. ***p < 0.001 when the TNBS + vehicle group was compared to any of the other three. E, Minocycline inhibits the decrease in LTD caused by peripheral inflammation (saline + vehicle, n = 5 slices, 5 rats; saline + minocyline, n = 4 slices, 4 rats; TNBS + vehicle, n = 6 slices, 4 rats; TNBS + minocycline, n = 4 slices, 4 rats). *p < 0.05 when the TNBS + minocycline group was compared to TNBS + vehicle.