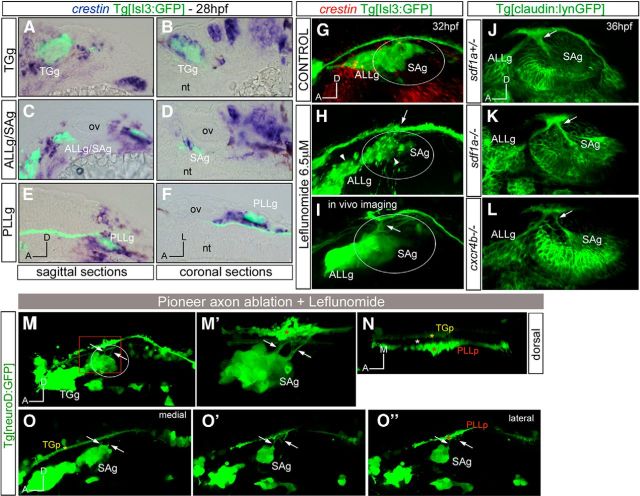
Figure 5.
Cooperation of pioneer axonal contacts and NCCs in the establishment of the entry points. A–F, Tg[Isl3:GFP] embryos were assayed for crestin in situ hybridization (blue). A, B, TGg. C, D, ALLg/SAg. E, F, PLLg. G–I, Tg[Isl3:GP] embryos were treated with DMSO (G) or leflunomide (H, I) and hybridized with crestin probe (G, H, red) or observed in vivo (I). Note that crestin expression is abolished in leflunomide-treated embryos, whereas sensory ganglia present defects in coalescence (H, white arrowheads). No effects in the entry points are observed, even in in vivo embryos (H, I, white arrows). J–L, Inhibition of NCC migration does not affect the entry point of SAg sensory axons at the central level: sdf1a−/−Tg[cldnb:lynGFP] (K) and cxcr4b−/−Tg[cldnb:lynGFP] (L) embryos were analyzed for ectopic entry points and compared with control embryos sdf1a+/−Tg[cldnb:lynGFP] (J). M–N, Tg[neuroD:GFP] embryos were treated with leflunomide and the first differentiated neurons from the ALLg/SAg were ablated using multiphoton microscopy. M, Lateral view showing ectopic entry points (white arrows). M′, Magnification of boxed region in M showing the ectopic entry points (arrows) in contact with the PLLp (red asterisk). N, Dorsal view of M′ showing the TGp (yellow asterisk), PLLp (red asterisk), and a lack of ALLp/SAp nerve bundle elongation (empty space marked with white asterisk). O–O″, Different single confocal planes from medial (O) to lateral (O″) showing that ectopic entry points now contact with the PLLp (red asterisk). Anterior is always to the left. Axes are indicated in the figure. The contour of the otic vesicle is indicated in white circles. ov, otic vesicle.