Figure 2.
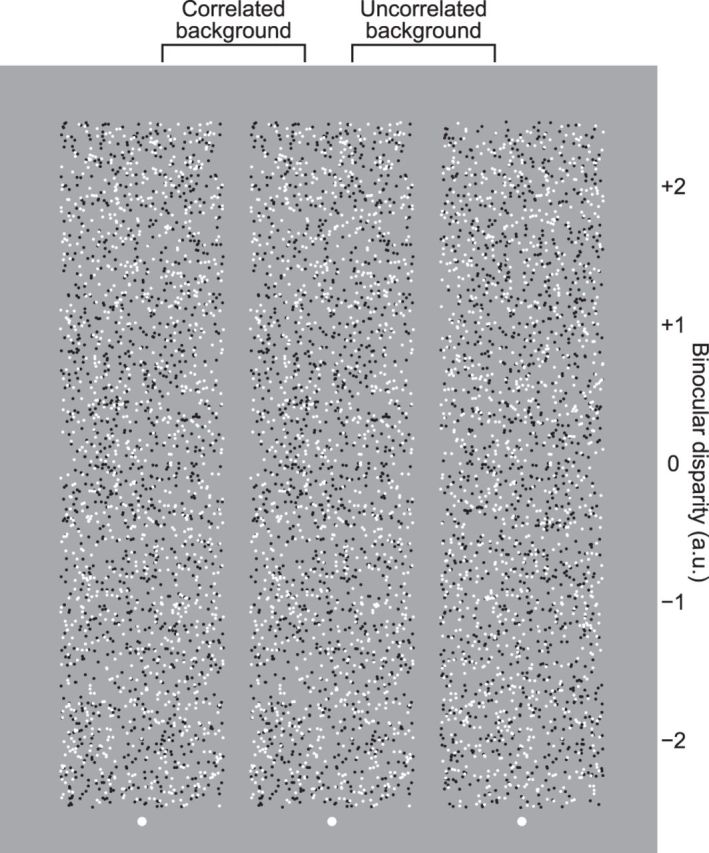
Examples of RDSs with uncorrelated and correlated surround dots. When one views the right and center dot patterns with the left and right eyes, respectively, five disks hovering among the background uncorrelated noise dots are perceived. When one views the center and left dot patterns with the left and right eyes, respectively, disks hovering on the background plane and holes in the background plane are perceived. Values on the right side of the RDS indicate the binocular disparity (arbitrary unit) when the stereogram is viewed cross-eyed.
