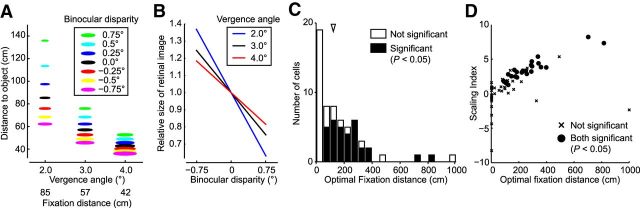
Figure 9.
Distribution of the optimal fixation distances for V4 neurons. A, The relationship between distance, binocular disparity, and retinal image size. Colors of the symbols represent the values of binocular disparity. Sizes of the symbols represent the relative size of the retinal image. When fixating on a point farther away, the degree of depth represented by binocular disparity becomes larger (e.g., compare the 85 cm case with the 57 cm case). B, The extent of change in retinal image size that occurred with the change in binocular disparity becomes larger for more distant fixations (i.e., smaller vergence angles). C, The distribution of the optimal fixation distances for each neuron. The arrowhead indicates the median of the distance parameter (118 cm). Filled columns represent significant scaling (sequential F test, p < 0.05). D, The relationship between the optimal fixation distance and the SI. The optimal fixation distance was positively correlated with the SI (Spearman's rank correlation, r = 0.74, p < 0.01).