Figure 7.
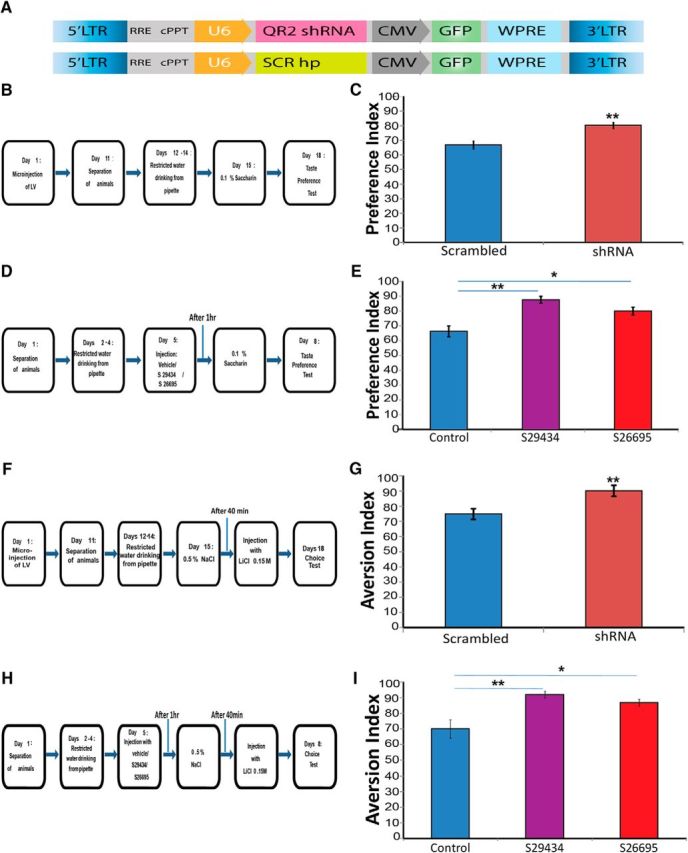
Decreasing either QR2 expression or activity enhances positive and negative novel taste learning. A, Structure of lentiviral vectors injected into the IC. Top, Vector containing QR2 shRNA injected to the test group. Bottom, Scrambled vector injected to the control group. B, Experimental design to determine the effect of reducing QR2 mRNA expression on novel taste memory. C, Animals injected with QR2 shRNA show significantly enhanced learning of the novel taste compared with control (scrambled, n = 12; shRNA, n = 10). D, Experimental design to determine the effect of inhibiting QR2 activity on taste memory. Animals were injected with QR2 inhibitors S29434 or S26695 (8 mg/kg, i.p.) or saline (control). E, Animals injected with either of the QR2 inhibitors display significantly enhanced learning of the novel taste compared with control (n = 8). F, Experimental design to determine the effect of reducing QR2 mRNA expression on negative taste memory (CTA). G, Animals injected with QR2 shRNA show significantly enhanced learning of the negative association of the novel taste compared with control (scrambled, n = 7; shRNA, n = 8). H, Experimental design to determine the effect of inhibiting QR2 activity on negative taste memory (CTA). Animals were injected with QR2 inhibitors S29434 or S26695 (8 mg/kg, i.p.) or saline (control). I, Animals injected with either of the QR2 inhibitors display significantly enhanced learning of the negative association of the novel taste compared with control (n = 8).
