Figure 2.
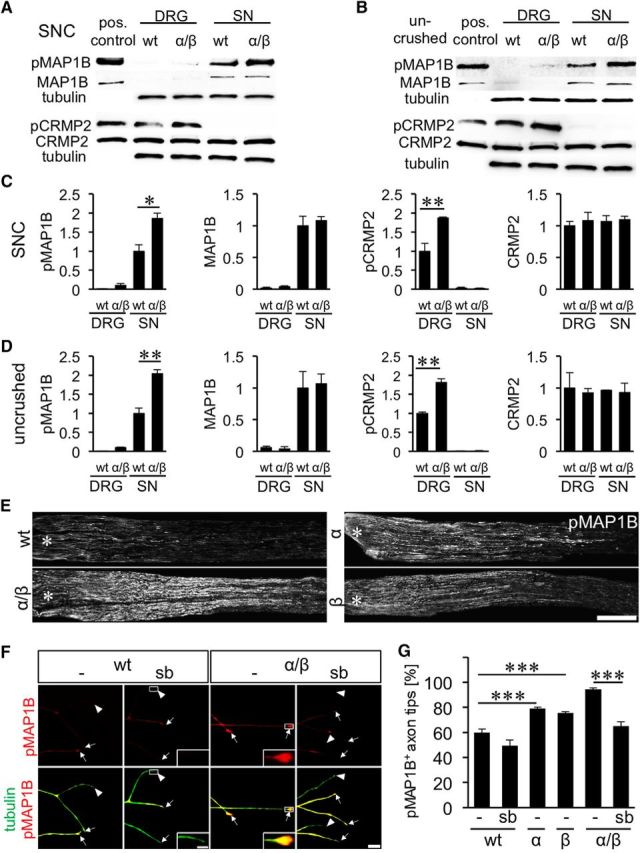
Effect of GSK3S/A on CRMP2 and MAP1B phosphorylation. A, B, Composition of Western blots analyzing levels of phosphorylated MAP1B (pMAP1B), total MAP1B, phosphorylated CRMP2 (pCRMP2), and total CRMP2 in DRG and sciatic nerves (SN), respectively, from wt and GSK3αS/A/GSK3βS/A (α/β) mice either 5 d after SNC (A) or in uninjured animals (B). Tubulin served as loading control. Lysates of HEK cells cotransfected with CRMP2 and constitutively active GSK3 served as positive controls for CRMP2 and pCRMP2, whereas HEK cells cotransfected with MAP1B and constitutively active GSK3 were used as positive control for pMAP1B and MAP1B. C, D, Quantification of Western blots as depicted in A and B. Consistent with increased GSK3 activity, MAP1B phosphorylation, but not total MAP1B, is increased in GSK3 knock-in mice. CRMP2 phosphorylation, however, is only elevated in DRG, despite abundant CRMP2 protein in sciatic nerves. Treatment effects: *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01. E, pMAP1B staining of longitudinal sciatic nerve sections of adult wt, α, β, and α/β mice 3 d after SNC verify MAP1B phosphorylation in regenerating axons. Scale bar, 500 μm. Asterisks indicate the crush site. F, Representative pictures of axons in DRG cultures of wt and α/β mice exposed to either vehicle (−) or 5 μm GSK3 inhibitor SB216763 (sb). Axons were stained for pMAP1B (red) and βIII-tubulin (tubulin, green). Arrows indicate pMAP1B-positive, arrowheads negative axon tips. Scale bar, 20 μm. Insets, Magnified examples of axon tips. Scale bar, 5, μm. G, Quantification of pMAP1B-positive axon tips of neurons from adult wt, α, β, and α/β mice exposed to either vehicle (−) or 5 μm GSK3 inhibitor SB216763 (sb). Data from transgenic neurons were normalized to wt controls and represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Treatment effects: ***p ≤ 0.001. GSK3S/A increased the percentage of pMAP1B in axon tips, which was abrogated by GSK3 inhibition using SB216763.
