Figure 10.
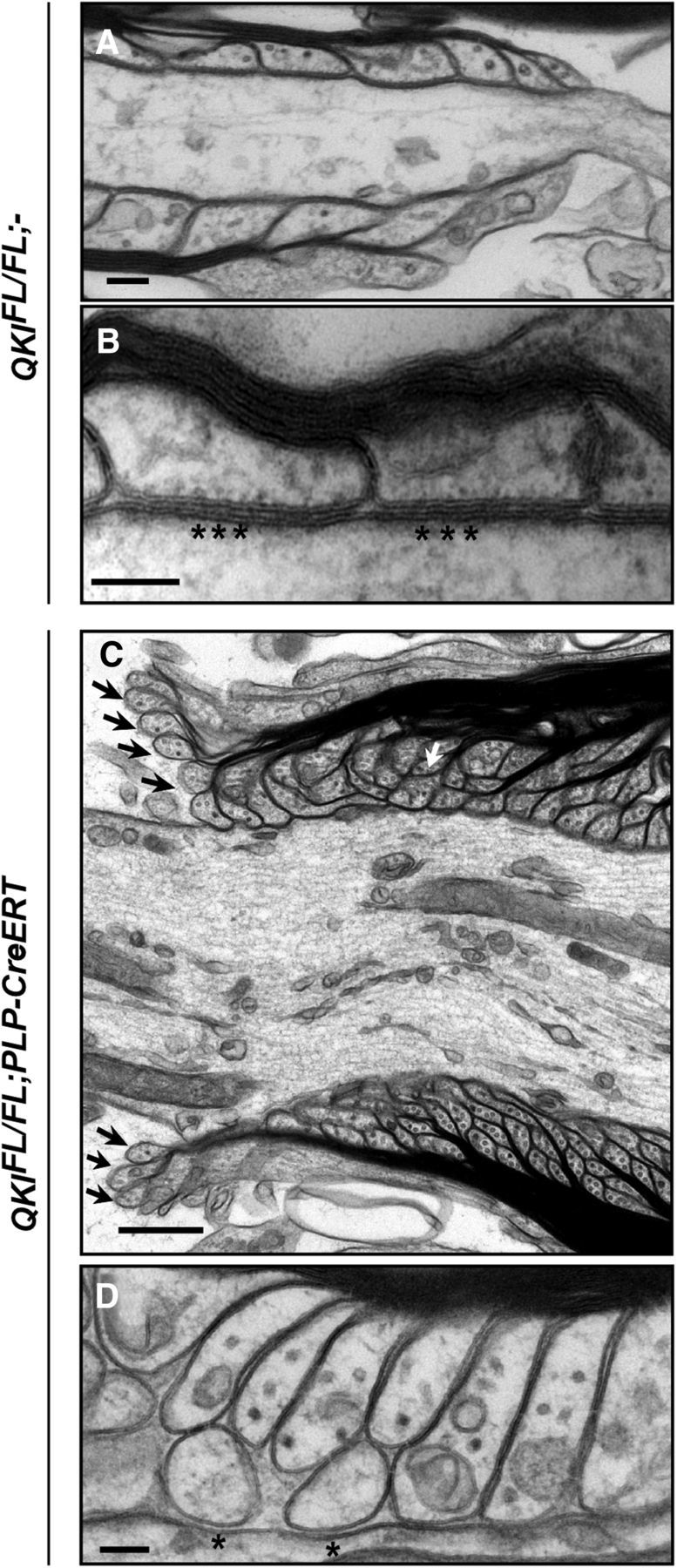
Ultrastructural paranodal defects in QKI-deficient mice. A, B, Representative electron micrograph images of longitudinal sections of spinal cords from wild-type mice at 30 d after OHT injection showing the attachment of paranodal loops to the axolemma and the formation of septate-like junctions (stars). Scale bar, 100 nm. C, Representative electron micrograph images of longitudinal sections of spinal cords from QKIFL/FL;PLP–CreERT mice displaying detached paranodal loops (black arrows) and the failure of several loops to terminate at the axolemma and instead abut each other (white arrow). Scale bar, 500 nm. D, Electron micrographs of QKIFL/FL;PLP–CreERT longitudinal spinal cord sections at 30 d after OHT injection showing the lack of septate-like junctions (stars) and increased space between the paranodal loops and the axolemma. Scale bar, 100 nm.
