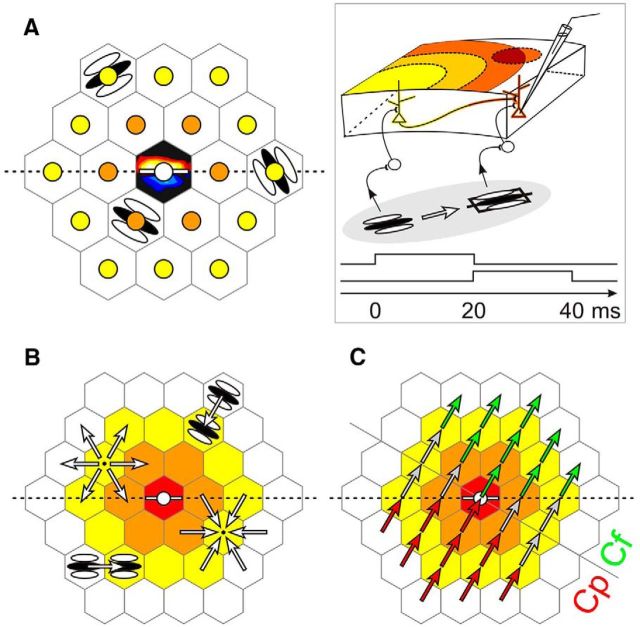
Figure 1.
Probing the synaptic integration field. A–C, The visual field was paved with a hexagonal lattice centered on the subthreshold RF. A, The RF is schematized by ON (red) and OFF (blue) subfields overlaid over the central tile (black). The size of the stimuli was chosen to be that of the RF. For each recorded cell, the lattice was positioned with a symmetry axis (dotted line) aligned along the cell's preferred orientation (white bar), represented by convention as the horizontal axis. The size of the hexagonal tiles was also chosen to be that of the RF, so that stimuli flashed in neighboring tiles could not overlap, and peripheral stimuli could not encroach on the RF. These conventions define a cellulocentric reference frame whose polar coordinates (relative eccentricity from the RF center, measured in number of tiles; and orientation from the preferred horizontal axis) are independent of the RF size or the absolute orientation preference of each cell. The “rings” of same relative eccentricity from the RF center are depicted by the colors of nodes or tiles. A, B, Sparse static (1S) and dynamic (2S) AM Gabor noises were applied in a randomly interleaved fashion to measure the static profile of the synaptic association field (S-AF) and its dynamic associative properties (D-AF), respectively. Gabor patches were each flashed for 20 ms. The 20 ms interval between stroke onsets was chosen based on previous reports of apparent horizontal propagation speed in cat V1 (Bringuier et al., 1999), to maintain the horizontal input and the feedforward drive on average in phase (see Box). A, Stimuli of six possible orientations were flashed at each node in the static protocol. Stimuli were presented in isolation, so that the center was not stimulated while peripheral nodes were explored. B, Each possible 2S-AM sequence converging onto or originating from each node was presented in the dynamic protocol, and defined a “trajectory” (white arrows). The 2S stimuli could either be in the ISO configuration (illustrated bottom left) or in the CROSS configuration (illustrated top right). C, A different parametric reading of the dynamic protocol. Acquisition records are grouped by motion flow direction and relative eccentricity of the AM trajectory. Trajectories along which relative eccentricity decreases are centripetal (Cp, in red), whereas those along which relative eccentricity increases are centrifugal (Cf, in green). Box inset, The working hypothesis is that the facilitatory effect of intra-V1 horizontal connectivity is maximal when the feedforward and horizontally mediated synaptic inputs reach in phase the intracellularly recorded cell.