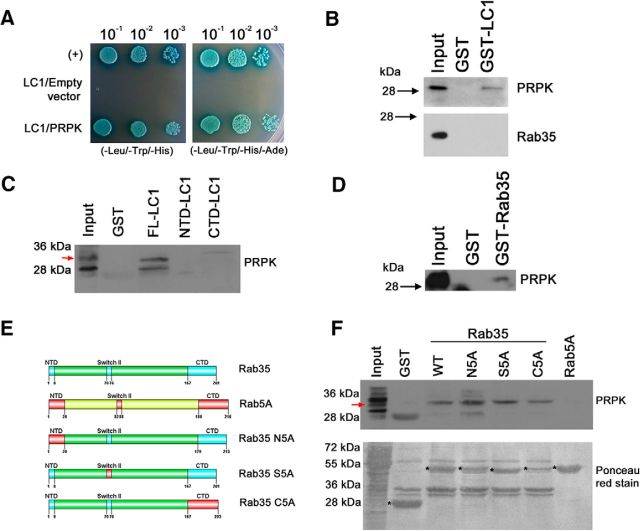
Figure 5.
PRPK interacts with LC1 and Rab35. A, Y2H binding assay with AH109 yeast cotransformed with pGBKT7-LC1 and pGADT7-PRPK. Yeast carrying pGADT7-T and pGBKT7–p53 were used as a positive control (+); yeast cotransformed with pGBKT7-LC1 and empty pGADT7 were used as a negative control. Yeast from all three cotransformations were grown in low-stringency TDO (-Leu/-Trp/-His) and high-stringency QDO (-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade) media supplemented with X-α-Gal. Decreasing dilutions were seeded and allowed to grow for 4 d. B–D, GST pull-down assay from (E18) rat brain protein extracts. GST-LC1 and GST alone were incubated with brain supernatants, and the bound fraction was analyzed by immunoblotting for PRPK (B, top) and Rab35 (B, bottom). GST pull-down assays using full-length LC1, and N- and C-terminal domains were incubated with brain supernatants and the bound fraction analyzed by immunoblotting for PRPK (C). GST-Rab35 and GST alone were incubated with brain supernatants, and the bound fraction was analyzed by immunoblotting for PRPK (D). E, Schematic representation of Rab35 (swapping motif in light blue) and Rab5 (swapping motif in red) protein domains. Swapping mutants for Rab35 (N5A, S5A, and C5A). The numbers refer to the amino acid positions in mouse Rab35 and their substitution by the corresponding motif of Rab5. F, GST pull-down assays using proteins described in E were incubated with brain supernatants, and the bound fraction was analyzed by immunoblotting against PRPK (top). Purified proteins are indicated with an asterisk in the Ponceau red-stained membrane (bottom).