Figure 1.
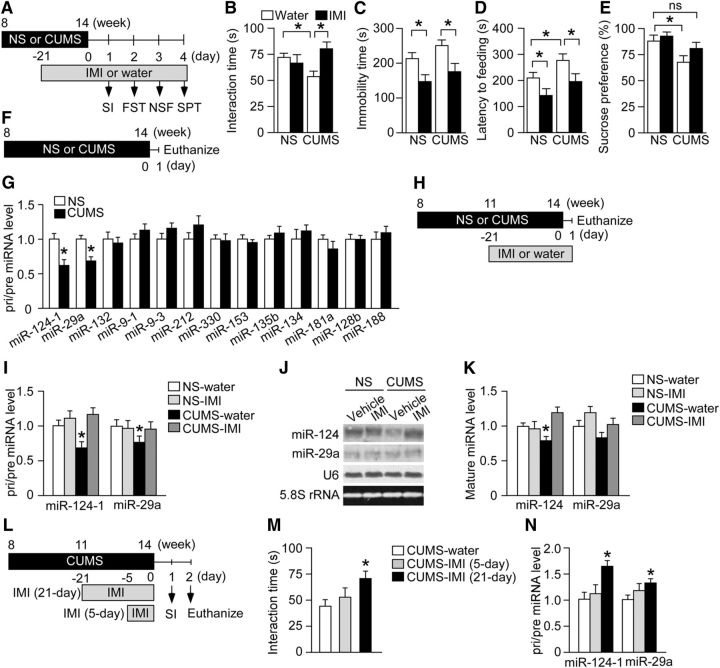
Chronic stress induces depression-like behaviors and miR-124 downregulation in the hippocampus. A, Schematic of the experimental design for assessing the effects of CUMS and antidepressant treatment on depression-like behaviors. Mice were subjected to CUMS for 6 weeks. The antidepressant IMI was administered orally during the last 3 weeks of the CUMS session. Stressed and NS mice receiving aqueous IMI or water were tested in behavioral assays. B–E, Results of behavioral tests. B, SI time in the SI. C, Immobility time in the FST. D, Latency to feeding in the NSF. E, Sucrose preference in the SPT. CUMS induced multiple depression-like behaviors compared with NS mice received water: reduced SI (B), enhanced latency to feeding (D), and reduced sucrose preference (E). n = 14–18 mice per group. *p < 0.05. ns, Nonsignificant. F, Schematic of the experimental design for analysis of stress-induced changes in hippocampal expression of brain-enriched pri/pre-miRNAs. Mice were subjected to CUMS for 6 weeks. Stressed and NS mice were then killed for hippocampal miRNA expression analysis. G, Levels of pri/pre-miRNAs in the hippocampus of mice subjected to CUMS or the NS condition (n = 6 mice per group). Pri/pre-miR-124-1 and -miR-29a expression levels were reduced by CUMS. *p < 0.05. H, Schematic of the experimental design for testing the effects of IMI on hippocampal miR-124 and miR-29a expression levels. Mice were subjected to a 6-week CUMS protocol with administration of water or IMI during the last 3 weeks and then killed for expression analysis. I, Levels of pri/pre-miR-124-1 and pri/pre-miR-29a in the hippocampus of mice subjected to CUMS or the NS condition and receiving either water or IMI for the last 3 weeks (n = 6 per group). CUMS-induced downregulation of both pri/pre miRNAs was blocked by IMI. *p < 0.05 versus NS-water. J, K, Levels of mature miR-124 and miR-29a in the hippocampus of mice subjected to CUMS or the NS condition and receiving either water or IMI for the last 3 weeks (n = 6 mice per group). Mature miR-124 expression, but not mature miR-29a expression, was downregulated by CUMS. This effect was blocked by IMI. *p < 0.05 versus NS-water. L, Schematic of the experimental design to test the effects of subchronic IMI on depression-like behavior and hippocampal miRNA expression. Mice were subjected to a 6-week CUMS session. IMI was administered during the last 21 d (chronic administration) or 5 d (subchronic administration) of the CUMS session. M, SI time of mice subjected to a 6-week CUMS session with or without IMI treatment (n = 12–14 mice per group). Only chronic IMI administration (21 d) significantly increased the SI time. *p < 0.05 versus CUMS-water. N, Levels of pri/pre-miR-124-1 and pri/pre-miR-29a in the hippocampus of stressed mice receiving subchronic or chronic IMI (n = 6 mice per group). Only chronic administration (21 d) significantly increased these miRNAs. *p < 0.05 versus CUMS-water. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.