Figure 10.
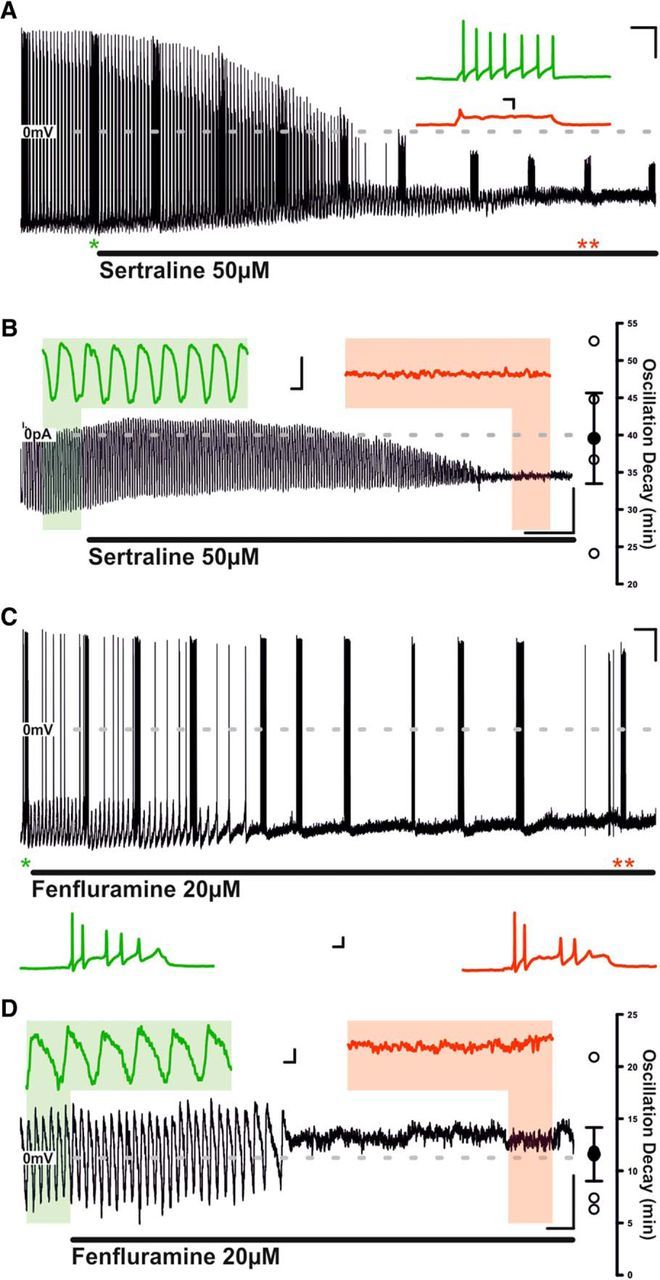
Sertraline abolishes both the TIDA oscillation and capacity for repetitive discharge, whereas fenlfuramine abolishes the TIDA oscillation but leaves the capacity for repetitive discharge intact. A, Current-clamp recording of an oscillating TIDA neuron. The response of the cell to injection of square-form–positive current pulses of constant size is tested at regular intervals (e.g., at asterisks). Prolonged bath application of sertraline results in gradual abolishment of oscillatory activity and reduction in AP amplitude and number, as well as of spontaneous discharge. Calibration: 20 mV, 2 min. Inset, Expanded sections from A denoted by asterisks. Calibration: Inset, 20 mV, 50 ms. B, Voltage-clamp recording of a TIDA neuron filtered at 1 Hz. Prolonged sertraline exposure results in a gradual amplitude reduction and eventual abolishment of oscillation. Calibration: 20 pA, 4 min. Inset, Expanded areas of B according to color. Calibration: Inset, 20 pA, 5 s. C, Current-clamp recording of an oscillating TIDA neuron. The response of the cell to injection of square-form–positive current pulses of constant size is tested at regular intervals (e.g., at asterisks). Prolonged bath application of fenfluramine results in gradual abolishment of oscillatory activity but fails to reduce capacity for repetitive discharge. Calibration: 20 mV, 2 min. Inset, Expanded sections from C denoted by asterisks. Calibration: Inset, 20 mV, 50 ms. D, Voltage-clamp recording of a TIDA neuron filtered at 1 Hz. Prolonged fenfluramine exposure results in a gradual amplitude reduction and eventual abolishment of oscillation. Calibration: 5 pA, 1 min. Inset, Expanded areas of D according to color. Calibration: Inset, 2 pA, 4 s. **p < 0.01.
