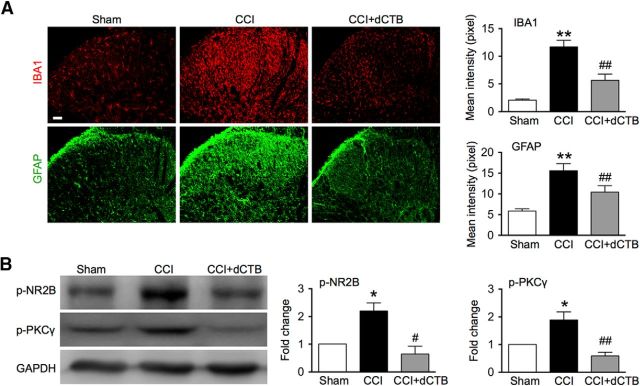
Figure 7.
Spinal administration of dCTB inhibits activation of glial cells in the spinal cord after CCI. A, Immunofluorescence showing effects of dCTB on activation of microglial cells (IBA1) and astrocytes (GFAP) after CCI. dCTB (1.6 mg) was given daily for 3 consecutive days starting 30 min before surgery and on postoperative day 11 for detecting its effect on IBA1 and GFAP, respectively. Tissues were collected 6 h after termination of the last injection (20 spinal cord sections in each group). Original magnification: 200×. Scale bars, 50 μm. B, Western blot showing effects of dCTB on phosphorylation of NR2B and PKCγ. dCTB (1.6 mg) was given once a day on postoperative days 11, 12, and 13. Tissues were collected 6 h after termination of the last injection (n = 4). One-way ANOVA, (A) IBA1: p < 0.0001, F = 26.84; GFAP: p < 0.0001, F = 12.89; (B) NR2B: p = 0.0080, F = 11.97; PKC: p = 0.0025, F = 12.51. *p < 0.05 versus sham. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus CCI.