Figure 3.
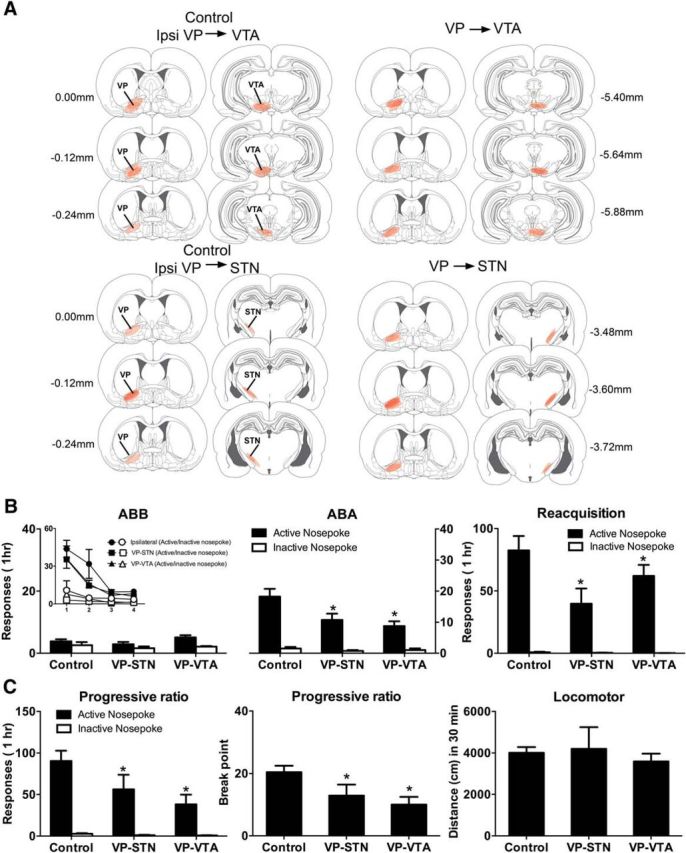
A, Location of hM4Di expression in VP, VTA, and STN for groups Control (n = 12), VP → VTA (n = 8), and VP → STN (n = 8). B, Mean (± SEM) responding on tests in the extinction (ABB) and training (ABA) contexts as well as during reacquisition. Inset, Responding during extinction training. There was significant context-induced reinstatement that was reduced in the VP → VTA and VP → STN disconnection groups, and this chemogenetic silencing also significantly reduced reacquisition of alcohol seeking. C, Mean (± SEM) responding on tests for PR and locomotor activity. Chemogenetic disconnection in the VP → VTA and VP → STN groups reduced responding and breakpoints but did not affect locomotor activity. *p < 0.05, significant difference between VP → VTA and VP → STN versus Control.
