Figure 6.
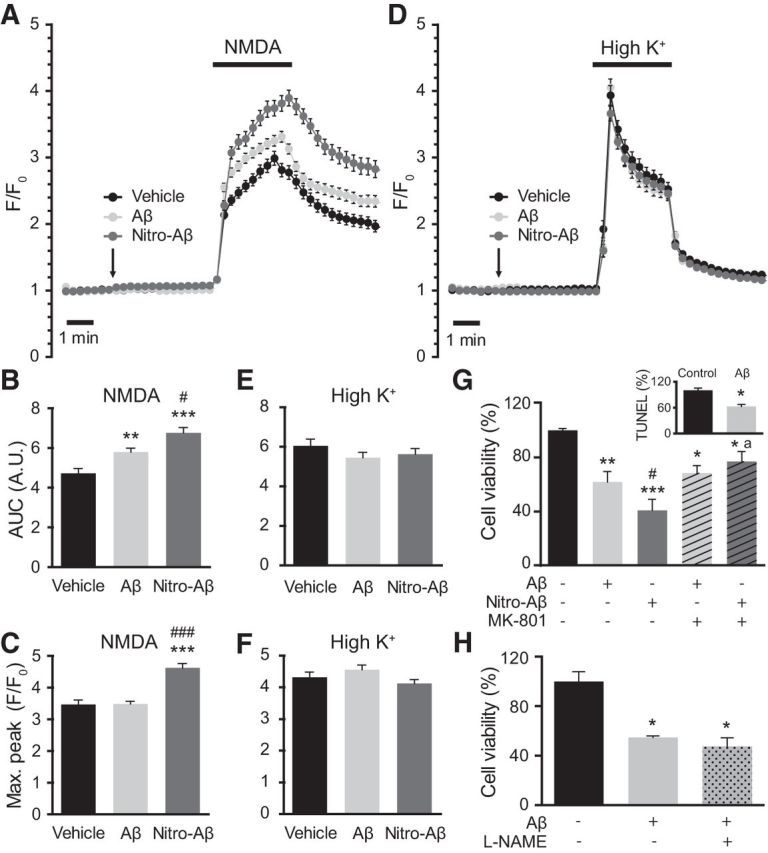
Nitro-Aβ oligomers affect calcium homeostasis and exert NMDA-dependent toxicity. Cells were treated for 5 min with 10 μm Aβ or nitro-Aβ and stimulated with bath application of either 100 μm NMDA (A) or 52.5 μm KCl (D). Mean ± SEM of 82–87 cells for NMDA and 98–104 for KCl. The area under the curve (AUC) (B, C) and the maximum response peak (E, F) were calculated for each cell response. G, Cell viability assay performed by the MTT method. Hippocampal neurons were treated with 10 μm Aβ and nitro-Aβ with or without 10 μm MK-801 for 5 min, and cell viability was assessed after 24 h. Untreated neurons were taken as 100% of viability. Inset, A control of Aβ toxicity studied by TUNEL assay. Mean ± SEM of three or four independent experiments. H, Cell viability assayed with the MTT method in hippocampal neurons treated with Aβ in the presence or absence of the NOS inhibitor l-NAME for 5 min. Cell viability was assessed after 24 h. Mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, compared with control (one-way ANOVA using Newman–Keuls post test). **p < 0.01, compared with control (one-way ANOVA using Newman–Keuls post test). ***p < 0.001, compared with control (one-way ANOVA using Newman–Keuls post test). #p < 0.05, compared with Aβ (one-way ANOVA using Newman–Keuls post test). ###p < 0.001, compared with Aβ (one-way ANOVA using Newman–Keuls post test). ap < 0.05 compared with nitro-Aβ by (one-way ANOVA using Newman–Keuls post test). Student's t test for the TUNEL study.
