Figure 6.
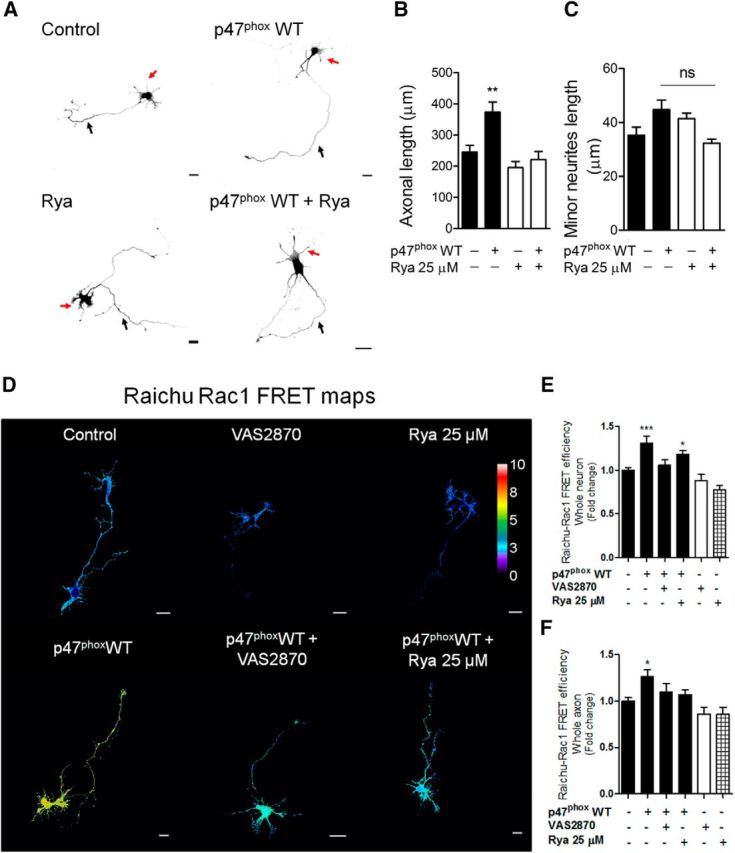
NOX gain-of-function increases both axonal development and Rac1 activity through a RyR-dependent mechanism. A–C, Neurons were cultured and transfected immediately after plating with GFP alone (control) or cotransfected with the p47phox WT construct. After 1 d of culture, neurons were treated with ryanodine (25 μm) and fixed at 3 DIV. A, Representative neurons after p47phox WT expression and ryanodine treatment. B, C, Quantification of axonal length (B) and minor neurite length (C) of neurons shown in A. B, **p < 0.01 versus control, Kruskal–Wallis test (n = 3). C, ns = nonsignificant, ANOVA, Dunnett's post test (45 were neurons analyzed for each condition). D, E, Neurons (1 DIV) were transfected with the Raichu-Rac1 probe alone (control) or together with the p47phox WT construct. After 1 d of expression, neurons were treated with VAS2870 (5 μm) or ryanodine (25 μm) for 1 h. Neurons were then fixed to evaluate FRET efficiency. D, FRET maps. E, F, Quantification of the FRET efficiency in control, VAS2870-, and ryanodine-treated neurons in whole neuron (E) and axon (F). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus control, ANOVA, Dunnett's post test (n = 3; 20 neurons were analyzed for each condition). Results are from 3 different independent cultures (n = 3). Scale bar, 20 μm.
