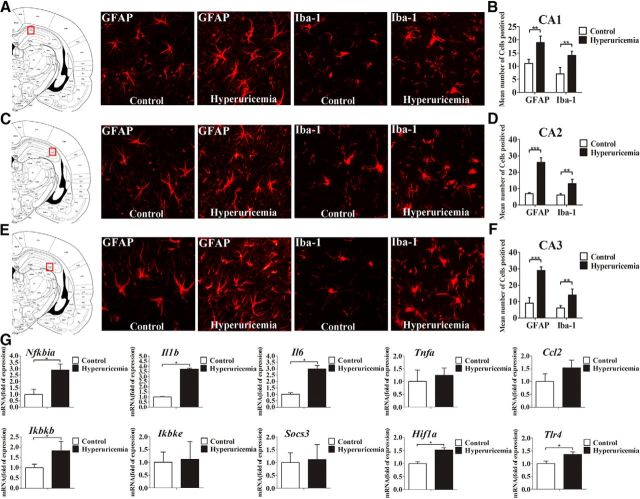
Figure 2.
Serum UA elevation results in chronic hippocampal neuroinflammation and gliosis. A–F, Hippocampal CA1 (A, B), CA2 (C, D), and CA3 (E, F) sections of the rats fed a standard chow or a HUAD were immunostained for GFAP (left) and Iba-1 (right). Immunofluorescence detection of the astrocytic marker GFAP protein and of the microglial marker Iba-1 in the rat hippocampus (4 μm) from rats fed either chow or a HUAD for 12 weeks. The image is displayed at 200× the original magnification and was used for the quantification of hippocampal astrocyte and microglia numbers. The mean numbers of hippocampal astrocytes and microglia in rats fed either chow or a HUAD were quantified in the regions displayed on the right (mean ± SEM; n = 6 rats per group). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs chow-fed controls. G, Time course of the induction of mRNA expression of inflammatory mediators, including proinflammatory cytokines (Il6, Il1b, Tnfa, Socs3, and Ccl2) and TLR4/NF-κB signaling (Tlr4, Nfkbia, Ikbkb, and Ikbke) in the hippocampi of rats that were fed chow or a HUAD for up to 12 weeks (n = 6 rats per group). All mRNA species were quantified relative to the expression of the housekeeping gene Gapdh and are presented as fold changes relative to chow-fed controls. All displayed values are reported as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs chow-fed control.