Figure 3.
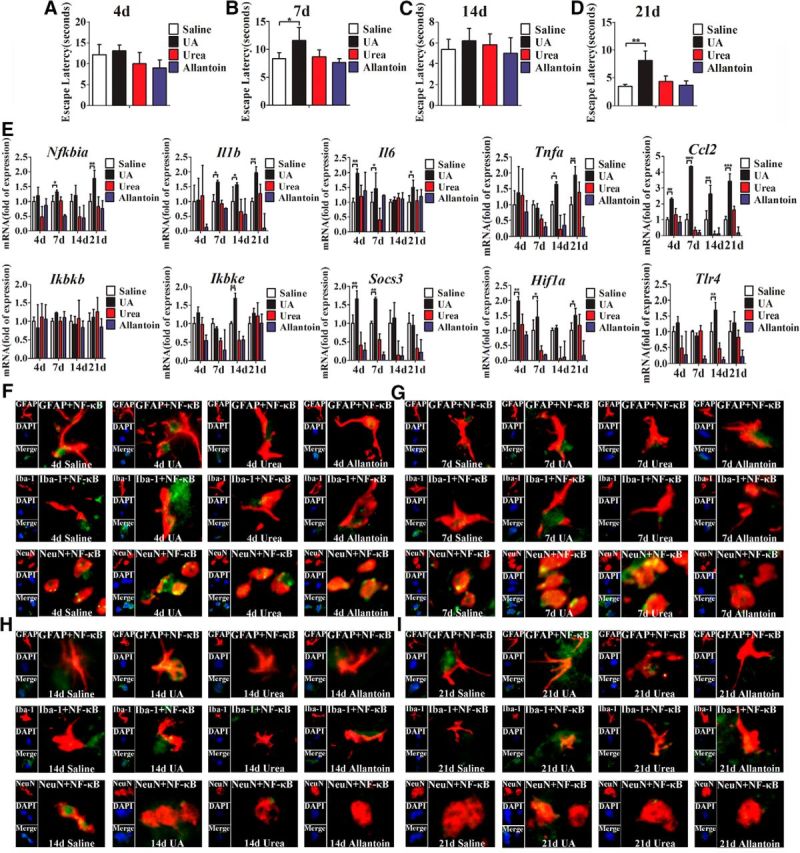
UA acts as an inflammatory stimulus and activates NF-κB in hippocampus. A–D, C57BL/6 mice were bilaterally injected with UA and implanted with a stainless steel guide cannula that targeted the hippocampus. Spatial learning of the mice was assessed in a Morris water maze after stereotactic injection of UA for 4 d (A), 7 d (B), 14 d (C), and 21 d (D), respectively. Each trial was presented as the average of four individual tests, and four trials were performed with the escape latency to the platform being recorded (Student's t tests, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, n = 6 rats per group). E, Time course of the induction of mRNA expression of inflammatory mediators, including proinflammatory cytokines (Il6, Il1b, Tnfa, Socs3, and Ccl2) and TLR4/NF-κB signaling (Tlr4, Nfkbia, Ikbkb, and Ikbke) in the hippocampi of mice that received stereotactic injection of saline, urea, allantoin, or 600 ng/ml UA for 4, 7, 14, and 21 d (n = 6 rats per group), respectively. All mRNA species were quantified relative to the expression of the housekeeping gene Gapdh and are presented as fold changes relative to saline controls. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs normal saline control. F–I, Hippocampal tissues were immunostained for GFAP and RelA, Iba-1 and RelA, and NeuN and RelA (400×) after 4 d (F), 7 d (G), 14 d (H), or 21 d (I) of exposure to saline, urea, allantoin, or 600 ng/ml UA. RelA was used for the reporting of NF-κB. DAPI nuclear staining revealed all cells in the section. GFAP, DAPI, Merge (DAPI + NF-κB), GFAP + NF-κB; Iba-1, DAPI, Merge (DAPI + NF-κB), Iba-1 + NF-κB; and NeuN, DAPI, Merge (DAPI + NF-κB), NeuN + NF-κB. All displayed values are presented as the mean ± SEM.
