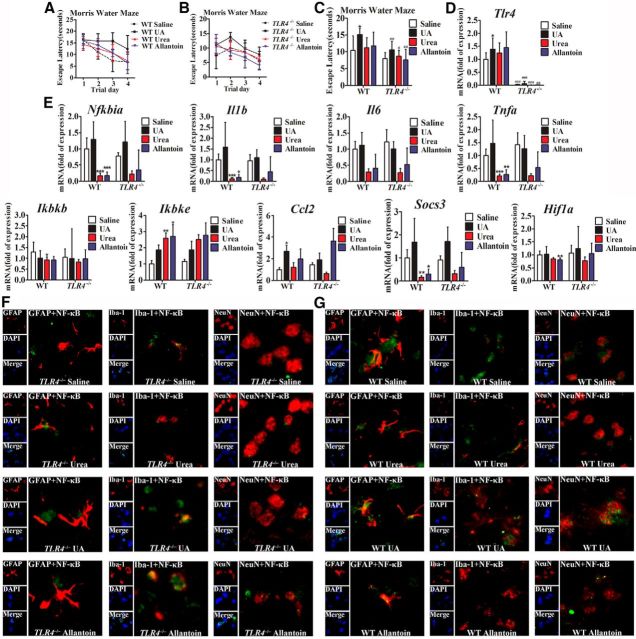
Figure 7.
TLR4/NF-κB signaling mediates UA-induced hippocampal inflammatory signaling and cognitive dysfunction. A–C, Spatial learning of WT and TLR4−/− mice with UA, as demonstrated by a Morris water maze. Each trial is presented as the average of four individual tests, and four trials were performed with the escape latency to the platform being recorded. D, E, The mRNA levels of inflammatory mediators, including proinflammatory cytokines (Il6, Il1b, Tnfa, Socs3, and Ccl2) and TLR4/NF-κB signaling (Tlr4, Nfkbia, Ikbkb, and Ikbke), were measured in hippocampus after exposure to saline, urea, allantoin, or 600 ng/ml UA for 21 d. F, G, Hippocampal tissues were immunostained for GFAP and RelA, Iba-1 and RelA, and NeuN and RelA (400×) after stereotactic injection of saline, urea, allantoin, or 600 ng/ml UA. RelA was used for reporting NF-κB. DAPI nuclear staining revealed all cells in the section (Student's t tests, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs WT saline control. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs WT normal control, n = 6 rats per group). GFAP, DAPI, Merge (DAPI + NF-κB), GFAP + NF-κB; Iba-1, DAPI, Merge (DAPI + NF-κB), Iba-1 + NF-κB; and NeuN, DAPI, Merge (DAPI + NF-κB), and NeuN + NF-κB. All displayed values are the mean ± SEM.