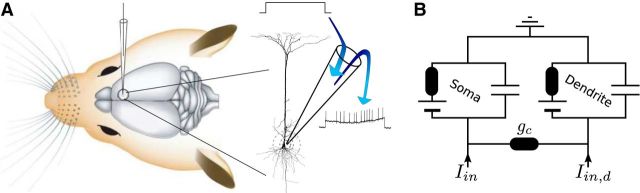
Figure 1.
Juxtacellular stimulation of a cortical neuron in vivo and the equivalent circuit used to mimic its response. A, Diagram of the juxtacellular stimulation. The electrode is inserted through the dura and brought into the close vicinity of a neuron. At high current densities/transmembrane voltages, the extracellular applied current stimulates the neuron via electroporation while the response is recorded simultaneously. B, Equivalent circuit of the two-compartment model. Each compartment consists of a resistor accounting for the inverse membrane conductance, a battery representing the resting potential, and a capacitance. Both compartments are connected via a coupling conductance gc. The injected current Iin(t) [Iin,d(t)] enters the somatic (dendritic) compartment.