Figure 1.
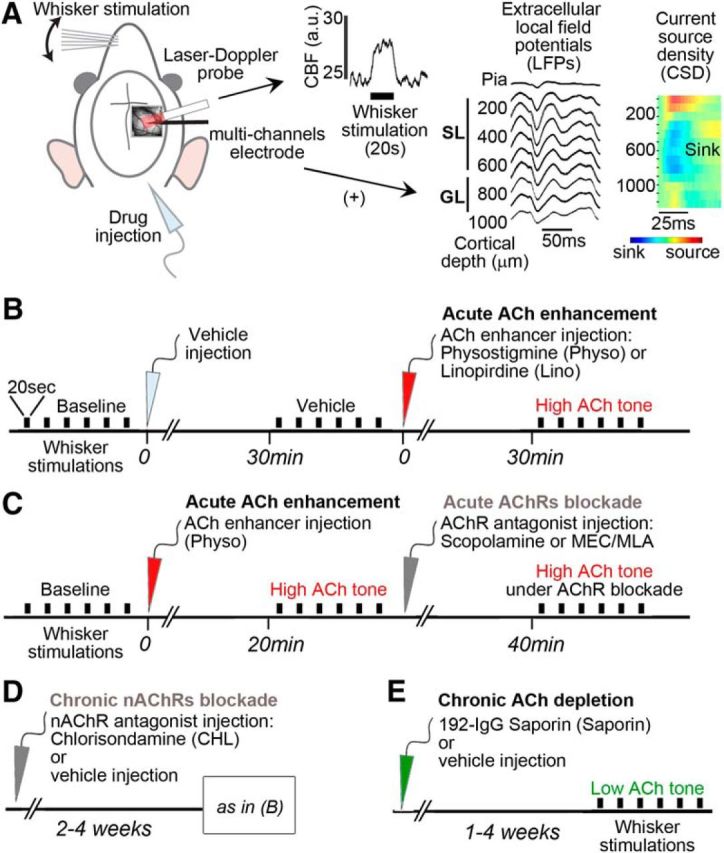
Schematic representation of the experimental procedures. A, In the first set of experiments (Fig. 2), cortical CBF was measured by a LDF probe placed over the thinned bone above the barrel cortex, as illustrated on a representative raw trace of a single 20 s whisker stimulation. In a parallel set of experiments (Figs. 3–5), a multicontact linear electrode was added (+) close to the LDF probe. To match the CBF and LFPs data, we analyzed the recordings channels of the electrode in the cortical layers matching the penetration of LDF, defined as SL and GL. Layer delineation was confirmed by large sink in the CSD profiles of the first evoked responses. B, Acute pharmacological ACh enhancement consisted in injections of respective vehicle (light gray arrow), followed by injection of ACh enhancers (red arrow): the AChE inhibitor physostigmine (Physo) or the ACh release enhancer Linopirdine (Lino). C, Timeline for acute ACh enhancement followed by acute blockade of AChRs (dark gray arrow) by either a mAChR antagonist (scopolamine) or a mixture of nAChR antagonists (MEC/MLA). D, Timeline for chronic blockade of nAChRs by CHL injected 2–4 weeks before CBF testing under enhanced ACh tone, as described above in B. E, For ACh depletion, rats were tested 1–4 weeks after intracerebroventricular injection of the specific cholinotoxin 192-IgG-Saporin (green arrow) or its vehicle (control group). Each rat was tested for only one drug or combination. The electrical BF stimulation protocol is not shown; see Materials and Methods for further details. Black bars indicate 20 s of whisker stimulation (six to 10 trials per condition). a.u., Arbitrary unit.
