Figure 1.
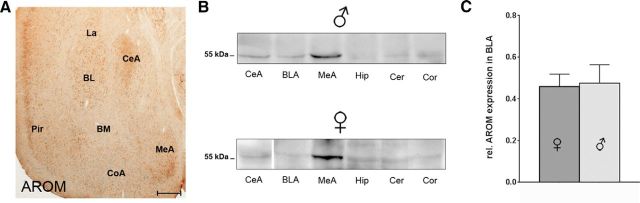
AROM expression in major subregions of rodent amygdala. A, Coronal section through anterior amygdala of an young adult mouse, immunostained for AROM using rabbit polyclonal antibodies (Yague et al., 2006). Substantial AROM expression is detectable in the MeA and CeA, in the BL and La nucleus of the BLA, and in the adjacent piriform cortex (Pir). Virtually, no AROM immunoreactivity is seen in the BM of BLA. Low levels of expression were found in the cortical amygdala (CoA). Scale bar, 250 μm. B, Western blots showing AROM protein expression in amygdala subregions CeA, BLA, and MeA of juvenile male and female rats using monoclonal antibodies against AROM (Acris). Tissue from hippocampus (Hip), cerebellum (Cer), and somatosensory cortex (Cor) was blotted for comparison. The strongest signal is found in the MeA. AROM expression levels in the CeA and BLA are comparable to levels in the hippocampus, neocortex, and cerebellum (note: a representative band for the female CeA was inserted from a different gel). C, Quantitative analysis of Western blot data, comparing AROM expression in BLA of age-matched (P20–P24) juvenile male and female rats. No difference between the sexes was evident (rel. expression of AROM: 0.46 ± 0.06 in females; 0.48 ± 0.09 in males; p = 0.88; n = 8 of each sex).