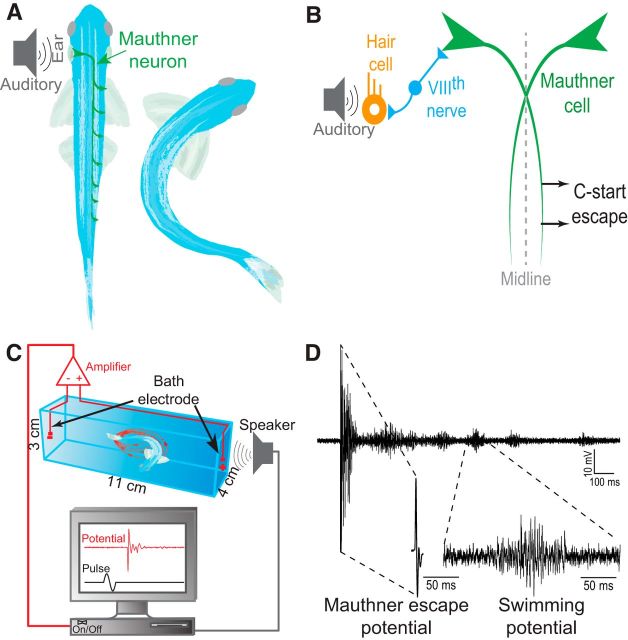
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrations of the M-cell escape circuit, experimental setup, and recording. A, Zebrafish startle response is activated by auditory stimuli. C-start behavior is mediated by the well-characterized Mauthner neural circuit. Activation of the M-cell is necessary for C-start escape. The M-cell innervates spinal cord motor neurons. B, Schematic illustration of the M-cell escape circuit. The M-cell escape response is initiated via activation of the VIIIth sensory nerve. C, A pair of bath electrodes is placed on either side of the testing chamber. Bath electrodes detect neuromuscular field potentials generated as the M-cell escape response is activated. M-cell escape is activated by an auditory pulse. Field potentials and stimuli are time locked and digitally recorded. D, An illustrative example of a phasic field potential recording recorded during activation of the C-start escape response mediated by the M-cell. This phasic response was followed by repeated swim bursts that were significantly lower in amplitude.