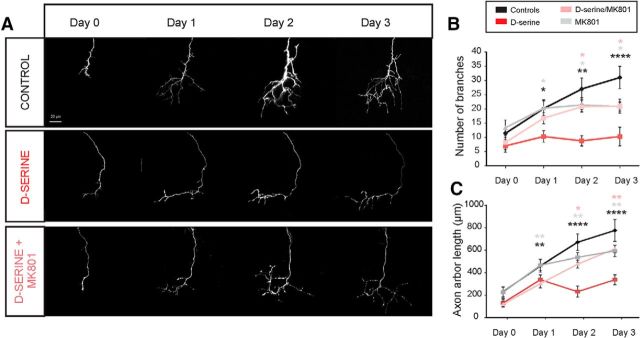
Figure 6.
d-Serine results in reduced growth and branching of axonal arbors. Daily in vivo imaging of individual retinotectal axon arbors in animals electroporated to express EGFP in RGCs. Repeated imaging over 3 d of exposure to rearing solution containing d-serine (100 μm) and/or the NMDAR antagonist MK-801 (10 μm). A, Individual examples show greatly reduced growth and branching of d-serine-treated axons, which is rescued by NMDAR blockade. B, Number of branch tips and (C) total axonal arbor length for control tadpoles (n = 7), tadpoles raised in d-serine (n = 6), MK-801 (n = 5), and d-serine + MK-801 (n = 7). *p < 0.05, d-serine-treated versus other groups (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post hoc test). ***p < 0.005, d-serine-treated versus all other groups (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post hoc test). ****p < 0.0001, d-serine-treated versus all other groups (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post hoc test). Black asterisk versus control. Gray asterisk versus MK-801. Pink asterisk versus d-serine + MK-801.