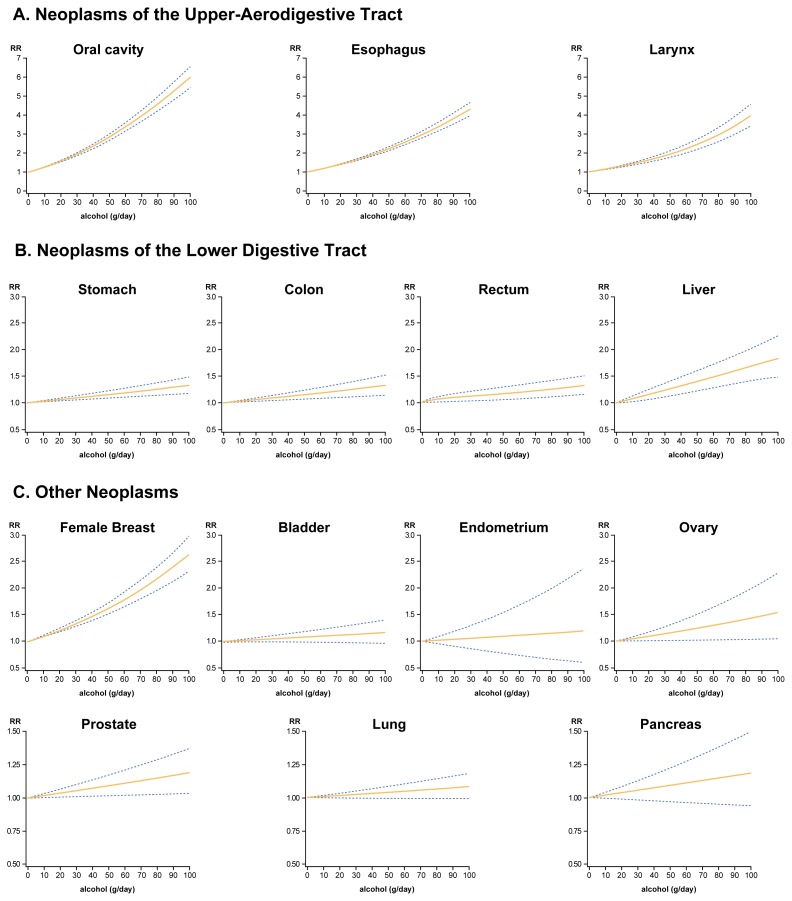
Relationship between increasing amounts of alcohol and risk (i.e., relative risk or RR) for 14 types of cancer. The RR describes the strength of the relationship between a variable (e.g., alcohol consumption) and a disease (e.g., cancer). The RR for the disease in people without the variable (e.g., abstainers) is defined as 1.0. A RR among the people with the variable (e.g., drinkers) of greater than 1.0 indicates that the variable increases the risk for the disease. The greater the value, the greater the risk. The curves shown here were obtained by fitting certain statistical models to the data from several studies (i.e., a meta-analysis). Blue dotted lines indicate 95-percent confidence intervals; that is, the range of RR that is 95 percent likely to show a true RR.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.