Figure 1.
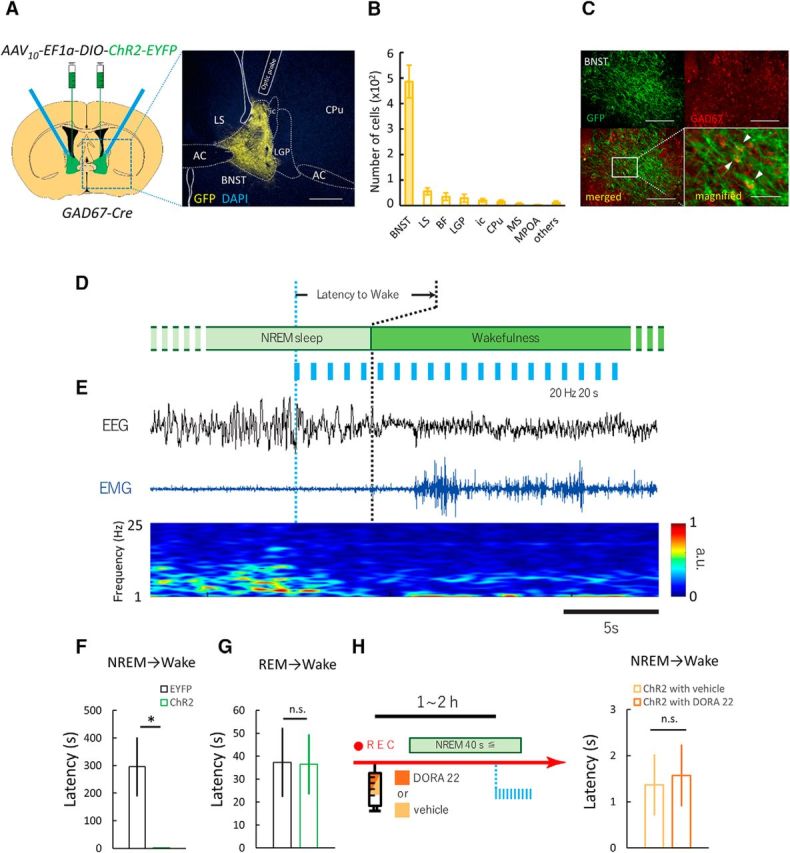
Optogenetic stimulation of GABABNST neurons induces immediate transition from NREM sleep to wakefulness. A, Optogenetic manipulation of GABA neurons in BNST. Left, Schematic representation of protocol. Right, Focal expression of ChR2-EYFP (yellow) in the BNST. White line shows placement of optic fiber tip. Scale bar, 250 μm. B, Numbers of EYFP-positive cells in various brain regions after injection of AAV10-EF1α-DIO-ChR2-EYFP in Gad67-Cre mice (n = 6). C, Top panels show fluorescent images of immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for GFP (green, top left) and in situ hybridization for GAD67 mRNA (red, top right). Scale bars, 200 μm. Bottom panels show merged images (left: ×10, right: ×20). Scale bars: left, 200 μm; right, 50 μm. D, Schematic drawing of experimental procedures. E, Representative EEG trace (top, black), EMG trace (middle, blue), and EEG power spectrum (bottom, color map; a.u., arbitrary unit) around stimulation point. Scale bar, 5 s. F, Effects of laser stimulation that induced immediate transition from NREM sleep to wakefulness. EYFP, n = 6; ChR2, n = 6; *p < 0.05, Welch's t test. G, Laser stimulation did not show any change in latency of REM sleep to wakefulness. EYFP, n = 6; ChR2, n = 6; n.s., not significant (p ≥ 0.05), Student's t test. H, Left, Schematic drawing of experimental procedures. Right, Laser-induced change in latency of NREM sleep to wakefulness transition after administration of DORA-22. Values are mean ± SEM. 3V, Third ventricle; AC, anterior commissure; LV, lateral ventricle.
