Figure 1.
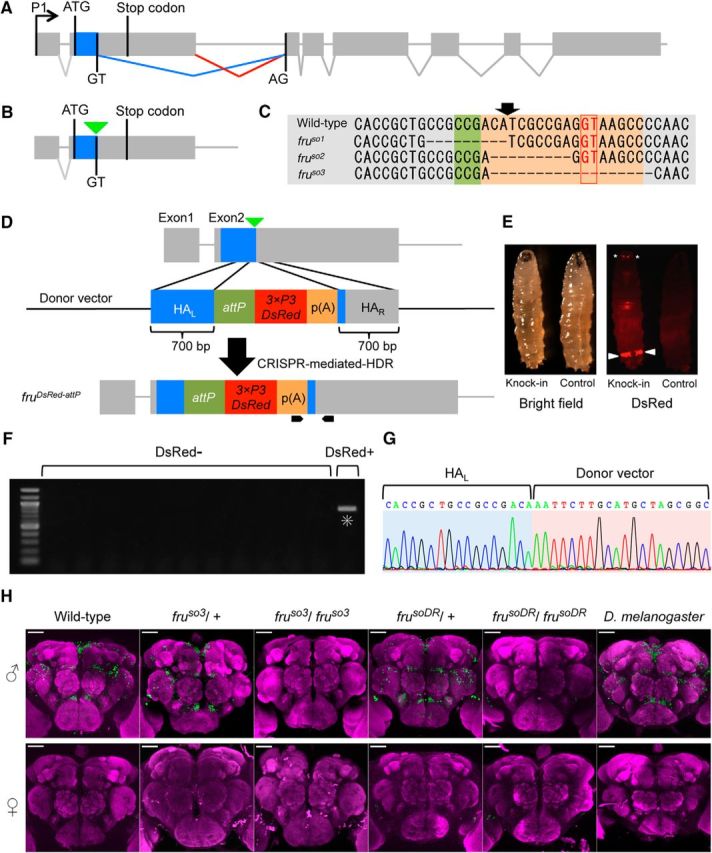
Generation of fru mutants in D. subobscura. A, The exon-intron organization of the fru gene in D. melanogaster, with the initiation and stop codons in the second exon as well as the splicing donor and acceptor sites for the conjunction of exon 2 and exon 3, highlighting the sex difference in fru splicing, which underlies the male-specific production of the full-length FruM protein. B, A schematic representation of the targeted site for gRNA (indicated by an inverted triangle) used for mutagenesis. C, The nucleotide sequence around the targeted region (shaded) that includes the splice donor site (boxed) in the wild-type genome (WT) and the induced deletion in the mutants fruso1, fruso2, and fruso3. The planned position for cutting is indicated with an arrow. D, A schematic representation of CRISPR-mediated knock-in targeting of the fru locus. The black pointed bars at the bottom indicate the position of the primers used for screening. HAL and HAR represent left and right homology arms, respectively. attP indicates the landing site for phiC31-integrase-mediated gene insertions. p(A) indicates a poly(A) signal sequence for the fluorescent marker gene 3xP3DsRed. E, Bright-field (left) and fluorescent (right) images of a third-instar larva expressing the DsRed protein (Knock-in) and a non-injected larva (Control). Arrowheads indicate anal pads and asterisks indicate Bolwig organs. F, Screening for CRISPR-mediated knock-in events by PCR. The left-most lane representing a sample derived from a DsRed+ fly but none of the other lanes from DsRed- flies had a band (highlighted with an asterisk) of the predicted size (905 bp) indicative of successful knock-in. G, The genomic sequence around the 5′ junction of HAL and the transgene of the DsRed+ fly. H, Anti-FruMale antibody immunoreactivity (green) of the male (top) and female (bottom) brains of D. melanogaster wild-type flies, D. subobscura wild-type and variants, i.e., fruso3 heterozygotes, fruso3 homozygotes, frusoDR heterozygotes, frusoDR homozygotes, and frusoDR homozygotes (from left to right), counterstained with nc82 (magenta). Scale bars, 50 μm.
