Figure 1.
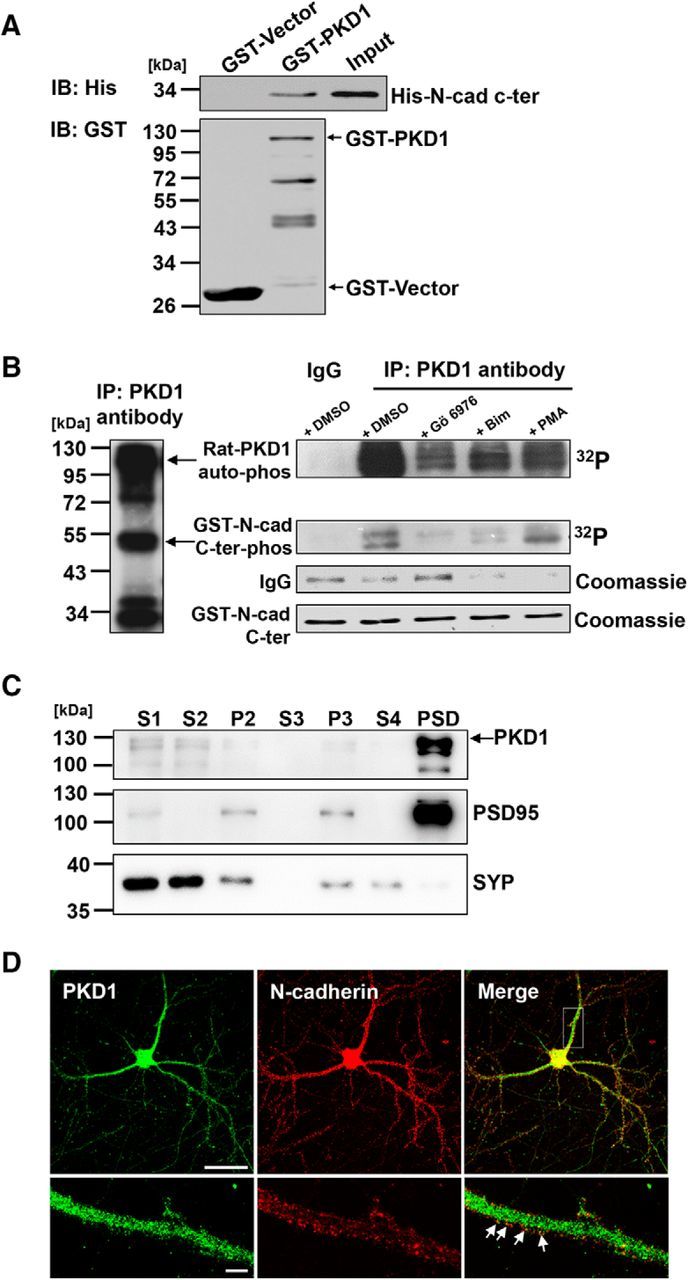
N-cadherin is directly associated with PKD1. A, IB of His-N-cad-c-ter pulldown by GST-PKD1 in vitro. Top, Probed for His-N-cad-c-ter binding to GST-PKD1. Bottom, Probed for total GST fusion protein present within each pulldown reaction. IB, Immunoblot. B, In vitro kinase assay showed that N-cadherin c-ter (N-cad 747–906) was phosphorylated by immunoprecipitated PKD1 (left) from the rat brain. The amount of the immunoprecipitated PKD1 was represented by the Coomassie staining IgG bands and indicated treatments were shown (right). Gö6976, a PKD1 inhibitor; Bim, a PKC inhibitor; and PMA, a PKC activator. C, Hippocampal CA1 region of rat brain lysates were fractionated by differential centrifugation, and subcellular fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to PKD1. S1, homogenates; S2, supernatant after P2 precipitation; P2, crude synaptosomes; S3, cytosol; P3, light membranes; S4, supernatant after PSD precipitation. SYP, synaptophysin; PSD95, post-synaptic density protein 95. D, Immunofluorescence staining for showing the colocalization of endogenous PKD1 and N-cadherin in DIV 15 hippocampal neurons. Arrows indicate the PKD1 puncta overlapping with N-cadherin. Scale bars: Top, 50 μm; Bottom, 5 μm.
