Figure 8.
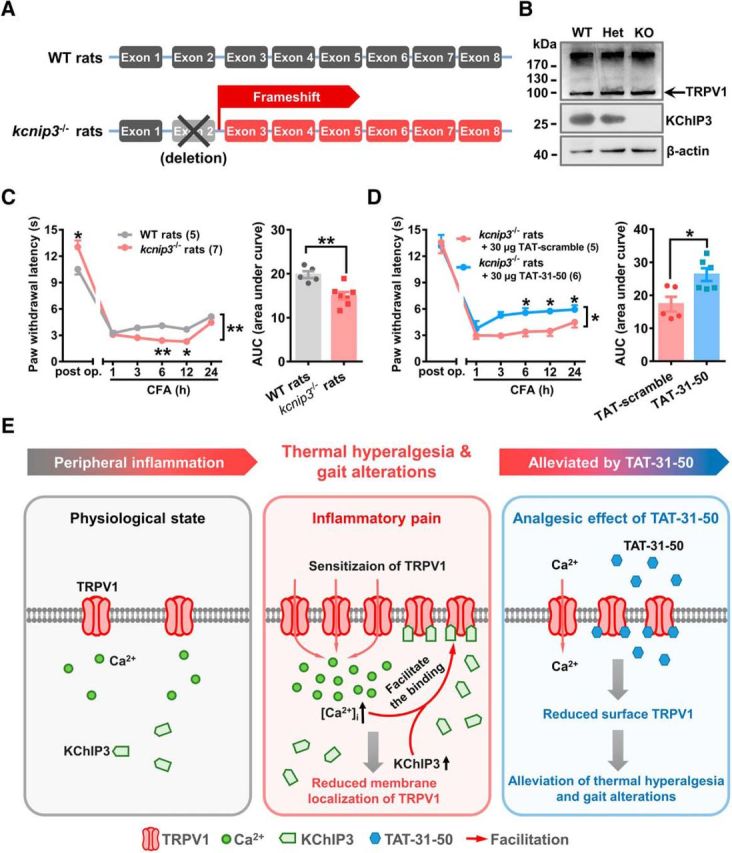
TAT-31-50 alleviates CFA-induced thermal hyperalgesia in kcnip3 KO rats. A, Schematic diagram of the genetic editing in kcnip3−/− rats. B, Representative Western blots of KChIP3 and TRPV1 in wild-type (WT), heterozygous (Het), and kcnip3 KO rats. C, D, Time course of the PWL of the ipsilateral hindpaw before and after CFA injection in WT and kcnip3 KO rats (C) or kcnip3 KO rats pretreated with an intrathecal administration of 30 μg of TAT-31-50 or TAT-scramble (D). C, D, Left, Two-way ANOVA, group effect: *p < 0.05, shown at the ends of the lines; post test: Sidak's multiple-comparisons test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, shown above the lines. Right, AUC values of the PWL time courses were compared between the WT and kcnip3 KO rats or the TAT-31-50- and TAT-scramble-injected rats. Unpaired t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. E, Schematic diagram of the inhibitory effect of KChIP3 and TAT-31-50 on TRPV1. Under physiological conditions, a low amount of TRPV1 is expressed on the plasma membrane. During inflammatory pain, TRPV1 undergoes functional sensitization and the intracellular [Ca2+]i is increased. Concurrently, expression of the KChIP3 protein is upregulated at 6 h after CFA injection. Therefore, binding between KChIP3 and the intracellular domains of TRPV1 is enhanced, which leads to a reduction in the surface localization of TRPV1 and the subsequent inhibition of TRPV1-mediated Ca2+ influx by KChIP3. Importantly, TAT-31-50, constructed based on the critical binding site of KChIP3 mediating its interaction with TRPV1, alleviates thermal hyperalgesia and gait alterations induced by intraplantar CFA injection significantly.
