Figure 8.
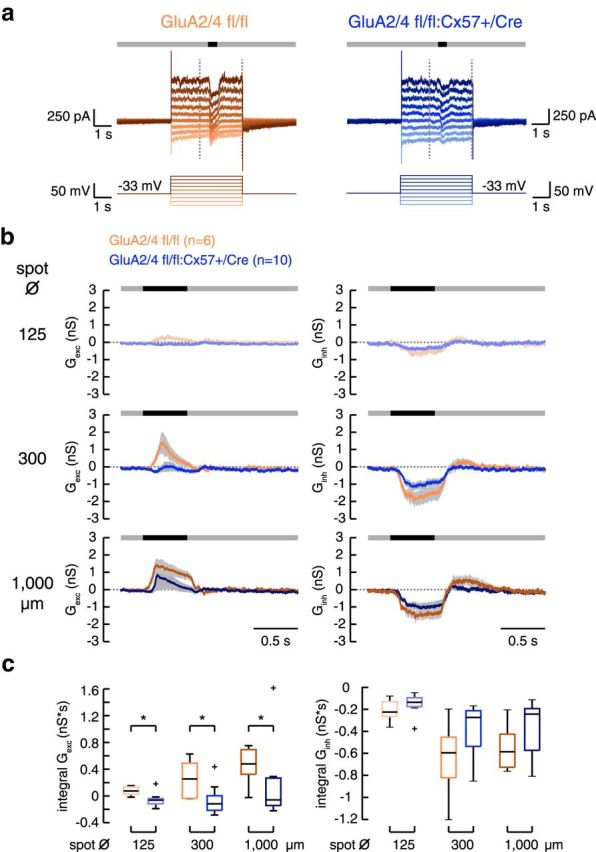
In GluA2/4-deficient mice, excitatory input to tOFF-αRGCs was strongly reduced. a, Examples of light-evoked membrane currents in tOFF-αRGCs from control and GluA2/4-deficient retinas. The cells were clamped from a holding potential of −33 mV to different potentials (−87 to +42 mV) in 15 mV steps. A spot of light decrement (here with a diameter of 300 μm) was presented on a gray background 2 s after clamping the cell to the new potential. The vertical dashed lines represent the time span shown in b. b, Mean excitatory and inhibitory conductances calculated from 6 and 10 tOFF-αRGCs from control and GluA2/4-deficient mice, respectively, for three different spot diameters. Shaded areas give SEM. c, Boxplots for the integrals of excitatory and inhibitory conductances in both genotypes. Outliers are represented by crosses. Excitatory conductances were significantly smaller in GluA2/4-deficient mice at all spot sizes (GluA2/4 fl/fl vs +/Cre, Wilcoxon rank sum test, p < 0.0225 for all comparisons). In contrast, inhibitory conductances were not significantly different (p > 0.1806 for all genotype comparisons, Wilcoxon rank sum test). *p < 0.05.
