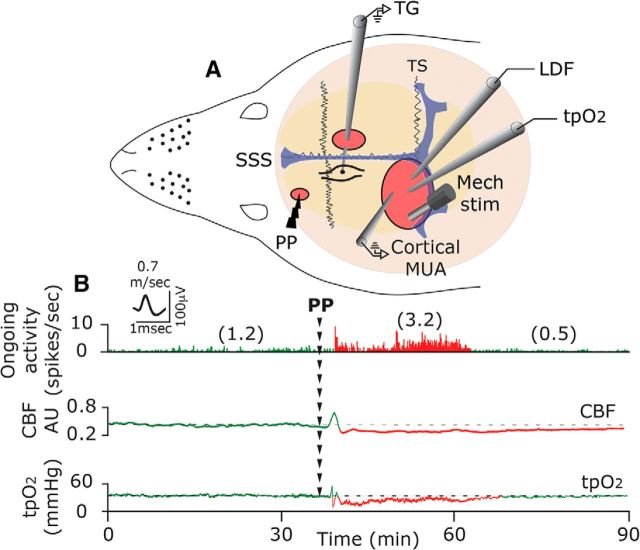
Figure 1.
A, Experimental setup: three skull openings (red ovals) were made. A small burr hole was made over the left frontal cortex to elicit a single CSD event using a pinprick (PP) stimulation. Meningeal afferent activity was recorded in the left trigeminal ganglion (TG) using a tungsten microelectrode inserted through a craniotomy made over the contralateral hemisphere. An ipsilateral craniotomy was made to expose a part of the left transverse sinus (TS) and superior sagittal sinus (SSS) and their vicinity to search for mechanosensitive meningeal afferents. Quantitative mechanical stimuli were delivered to the receptive field of afferents using a feedback-controlled mechanical stimulator. A Laser Doppler Flowmeter (LDF) probe was placed over the cortex near the receptive field of afferents to record changes in CBF and validate the induction of CSD noninvasively. In some animals, we also recorded the induction of CSD by monitoring multiunit activity (MUA) of cortical neurons. An oxygen microelectrode was placed in the superficial cortex to record CSD-evoked changes in cortical tpO2. B, Example of raw data recording depicting the activation of a C afferent meningeal afferent (with an overdrawn spike waveform used for data analysis) following the elicitation of CSD with a PP during the prolonged reduction in CBF and tpO2. The afferent recording trace represents a peristimulus time histogram (1 s bin-size). Average ongoing activity rate (spikes/s) are denoted in parentheses. The activation phase and associated cortical hypoperfusion and reduced tpO2 are colored red. LDF values are in arbitrary units (AU). stim, Stimulus.