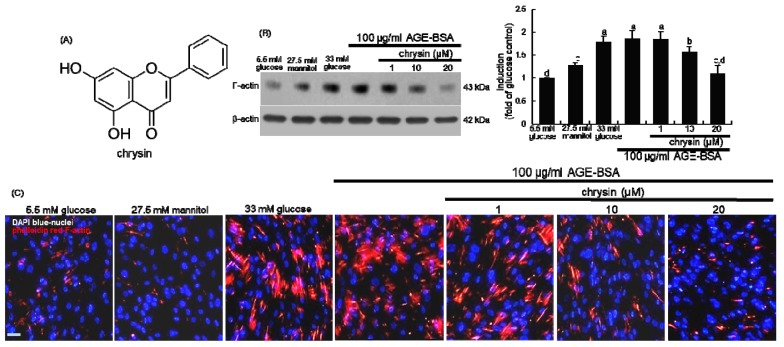
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of chrysin (A), and inhibition of F-actin induction by chrysin in advanced glycation end products (AGE)-bovine serum albumin (BSA)-exposed human renal mesangial cells (HRMC, B and C). HRMC were challenged with 5.5 mM glucose, 5.5 mM glucose plus 27.5 mM mannitol as osmotic controls or with 33 mM glucose or 100 μg/mL AGE-BSA in the absence and presence of 1–20 μM chrysin. The F-actin induction was measured by Western blot analysis using cell lysates with a primary antibody of F-actin (B). β-Actin protein was used as an internal control. Representative blots shown are typical of three independent experiments. The bar graphs (mean ± SEM) in the right panel represent quantitative results obtained from a densitometer. Values not sharing a letter are different at p < 0.05. Red-rhodamine phalloidin staining for F-actin formation was conducted in AGE-BSA-exposed HRMC (C). Nuclear counter-staining was done by using blue 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Scale bar = 50 µm. Each photograph is representative of at least four animals. Magnification: 200-fold.