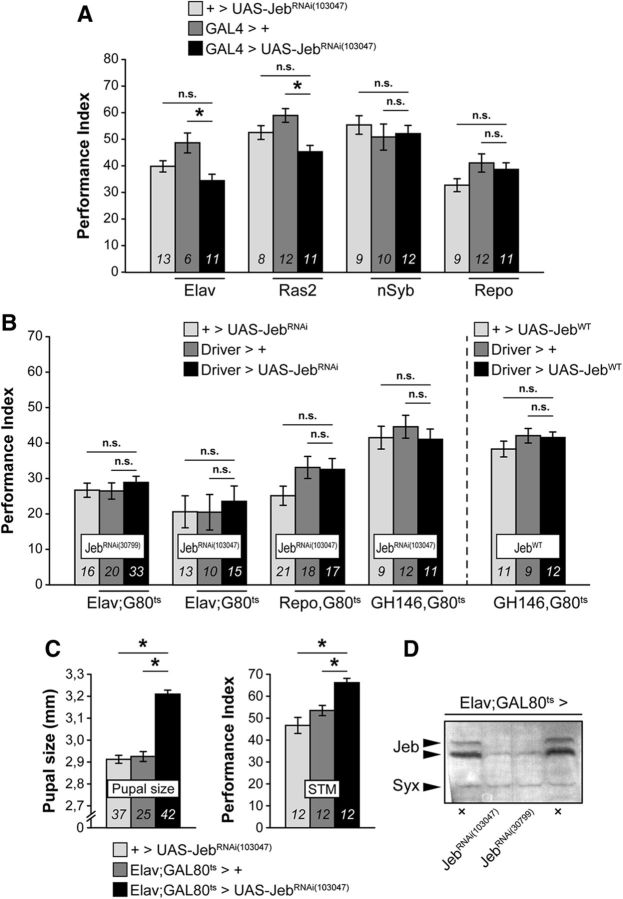
Figure 6.
The dAlk-activating ligand Jeb is not involved in LTM. Mean PIs (bars) ± SEMs (error bars) are shown. The number of experimental replicates (n) are indicated within the bars. *Significant differences denoted by horizontal line pairs. n.s. means not significant. A, Attenuation of Jeb expression levels with the JebRNAi(103047) transgene (black bars) did not affect 24 h LTM performance compared with controls (light and dark gray bars) when the transgene was expressed pan-neuronally or in glial cells only using the indicated Gal4 drivers. B, Attenuation of Jeb expression levels with the JebRNAi(103047) transgene restricted to the adult CNS for 48 h before training also did not affect 24 h LTM when the transgene was expressed pan-neuronally, in glial cells or in projection neurons using the indicated G80ts drivers. Lack of LTM effects was verified with pan-neuronal expression (Elav;Gal80ts) of a second independent JebRNAi(30799) transgene. Jeb overexpression (JebWT) in projection neurons (GH146,Gal80ts) also did not affect 24 h LTM. C, Pan-neuronal Jeb attenuation with the JebRNAi(103047) transgene yielded a substantial increase of pupal size compared with controls when the transgene was expressed throughout development and yielded a substantial increase of learning/3 min memory (STM, 1 cycle of 3 CS/US pairings) when the transgene was expressed only during adulthood for 2 d before conditioning. D, Representative semiquantitative immunoblot showing a dramatic reduction of endogenous Jeb levels upon pan-neuronal expression of both independent JebRNAi transgenes (UAS-JebRNAi(103047) and UAS-JebRNAi(30799)). Jeb protein (Jeb) was revealed with the anti-Jeb antibody (Jeb), and Syntaxin (Syx) was used as loading control.