Figure 15.
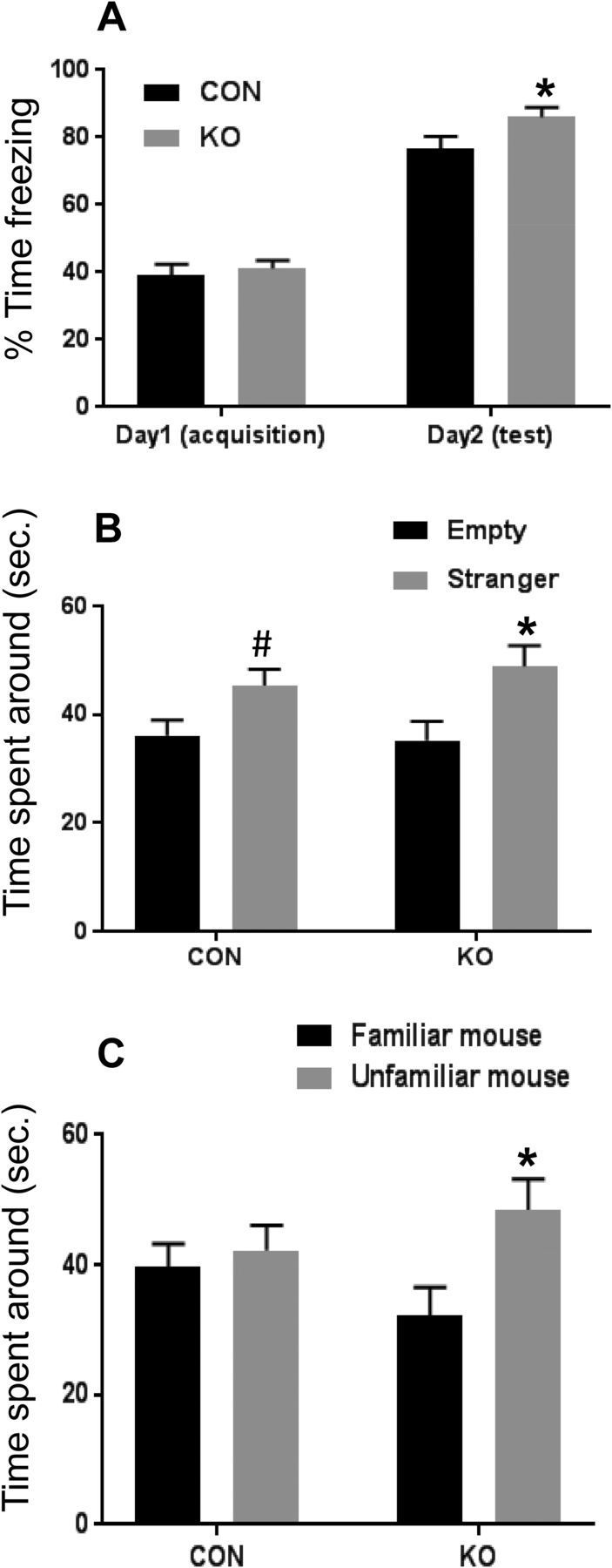
Contextual fear conditioning. A, CON mice showed impaired contextual fear conditioning. KO mice froze more during conditioning in the context of fear, whereas CON mice showed significantly lower levels of freezing (KO: n = 19 mice, CON: n = 22 mice, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple-comparisons test: interaction, F statistic [df: 1, 39] = 3.263, p = 0.0786; day 1 to day 2, F statistic [df: 1, 39] = 282.9, p < 0.0001; genotype, F statistic [df: 1, 39] = 7.47, p = 0.0094: *p-value for day 2 = 0.0033). B, C, Social interaction task. B, In the sociability phase, both CON and KO mice spent significantly more time with novel mouse than an empty wire cup, two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD test: interaction, F statistic [df: 1, 82] = 0.4447, p = 0.5068; time spent around, F statistic [df: 1, 82] = 12.16, p = 0.0008; genotype, F statistic [df: 1, 82] = 0.1687, p = 0.6823 (KO; n = 21 mice, *p-value = 0.0047, CON; n = 22 mice, #p-value = 0.047). C, At the social recognition phase, CON mice spent similar time with either the novel mouse or familiar mouse from the previous phase, whereas glut3 KO mice showed a significant trend toward the novel mouse rather than the familiar mouse, two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD test, CON; n = 22 mice, KO; n = 21 mice: interaction, F statistic [df: 1, 82] = 2.987, p = 0.0877; Time spent around, F statistic [df: 1, 82] = 5.23, p = 0.0248; genotype, F statistic [df: 1, 82] = 0.027, p = 0.8699. In the unfamiliar versus familiar of KO, *p = 0.0063.
