Figure 3.
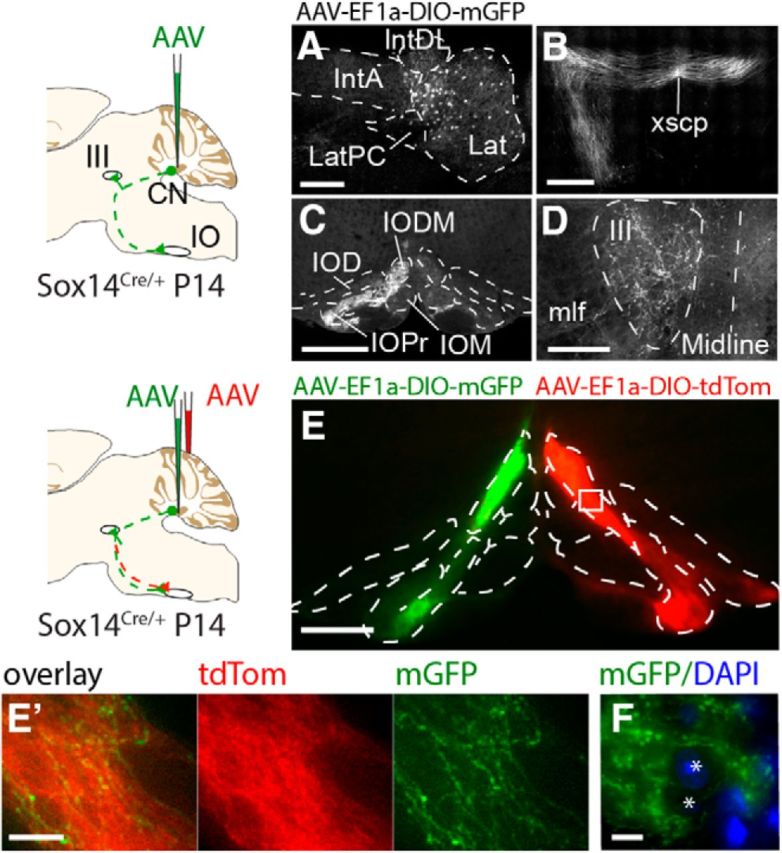
Anterograde labeling of Sox14 projections identifies targets in the midbrain and inferior olive. A–D, Unilateral injections of AAV-EF1a-DIO-mGFP targeted the lateral cerebellar nucleus (A), and projections were observed crossing the midline at the decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle (xscp, B) and terminating in the contralateral inferior olive (C) and the ipsilateral oculomotor nucleus (III, D). E, F, Bilateral injections of AAV-EF1a-DIO-mGFP and AAV-EF1a-DIO-TdTomato into the lateral cerebellar nucleus on either hemisphere show that axonal projections from each cerebellar hemisphere are bilateral, targeting both the ipsilateral and contralateral inferior olive though denser fluorescence on the contralateral side (E). Although the projections clearly terminate in the contralateral olive, axons with synaptic boutons can be seen in the ipsilateral side contacting the same range of cells. A higher-magnification view is shown in E′. F, High magnification image shows mGFP-expressing axons bypassing spaces where olivary cells reside (shown by blue DAPI staining, asterisks). Scale bars: E′, F, 20 μm; A, E, 200 μm; B–D, 500 μm. Lat, Lateral nucleus; LatPC, parvicellular lateral nucleus; IntDL, dorsolateral interposed nucleus; IntA, anterior interposed nucleus; IO, inferior olive; IOD, inferior olive dorsal nucleus; IODM, inferior olive dorsomedial cell group; IOM, inferior olive medial nucleus; IOPr, inferior olive principal nucleus; CN, cerebellar nucleus; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle.
